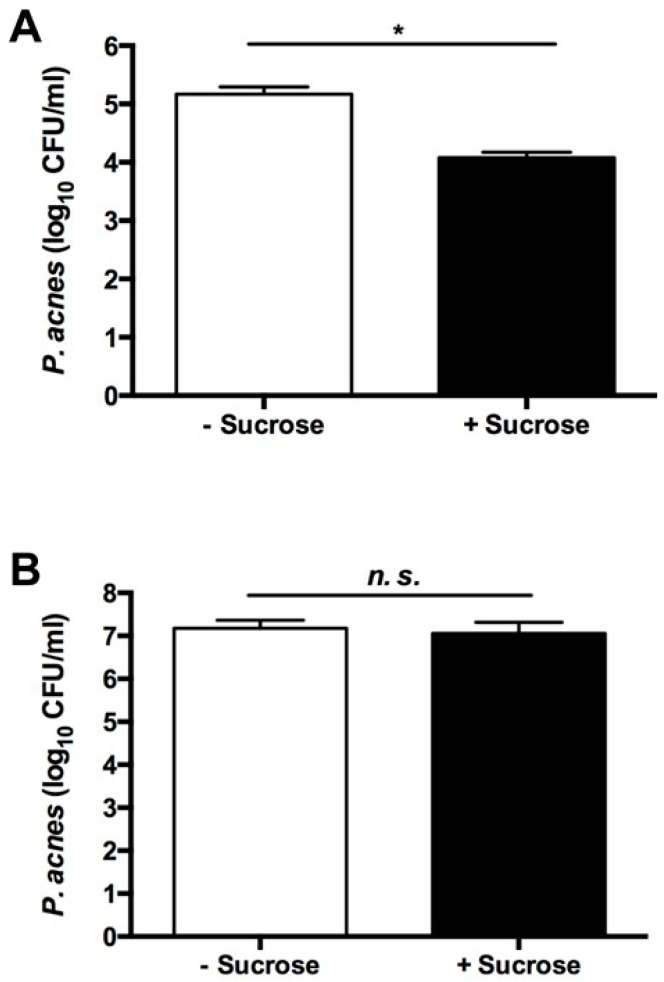
Figure 2.
The essential role of sucrose fermentation of S. epidermidis in the inhibition of the growth of P. acnes. (A) Fermenting S. epidermidis (ATCC 12228) or (B) non-fermenting S. epidermidis (106 CFU) were co-incubated with P. acnes (106 CFU) in 10 mL rich media with or without 20 g/L sucrose for three days. After incubation, culture media containing bacteria were diluted 1:10–1:105 with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then spotted the dilution (5 μL) onto P. acnes selective agar plates which contain rich media and 10 μg/mL of furazolidone. The number of P. acnes six days after incubation is expressed as log10 CFU/mL. Data are the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three separate experiments. * p < 0.05 (two-tailed t-tests). n.s. = not significant.