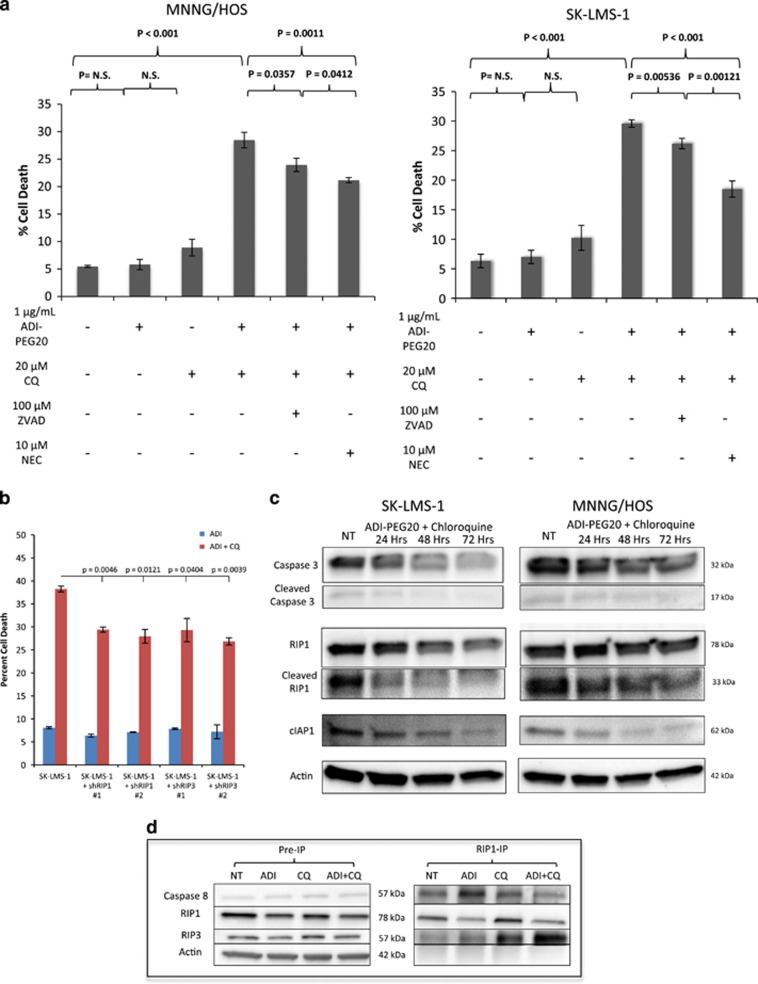
Figure 5.
Induction of necroptosis upon simultaneous arginine deprivation and chloroquine treatment. (a) Cell death as measured by FACS analysis after propidium iodide uptake. MNNG/HOS (left) and SK-LMS-1 (right) cells treated with 1 μg/ml ADI-PEG20, 20 μM chloroquine, both, or in combination with 100 μM ZVAD (an apoptosis inhibitor) or 10 μM necrostatin (a necroptosis inhibitor). Protection of cell death was more effective with necrostatin, indicating cell death is occurring primarily via necroptosis. (N=3). Data represented as mean±S.D. (b) Cell death as measured by FACS analysis after propidium iodide uptake in wild type, shRIP1 or shRIP3 SK-LMS-1 cells after treatment with 1 μg/ml ADI-PEG20 with or without 20 μM chloroquine. RIP kinase knockdown protected from induction of cell death, indicating necroptosis induction upon dual agent treatment. Data represented as mean±S.D. (N=2). (c) Western blots of SK-LMS-1 and MNNG/HOS cells untreated, or treated with ADI-PEG20 and chloroquine for 24, 48 or 72 h. In the presence of chloroquine and ADI-PEG20, the loss of the proapoptotic cleaved caspase 3 and the anti-necroptotic cIAP1 increases the threshold for apoptosis signaling while priming cells for death by necroptosis. Decrease in levels of cleaved RIP1 further suggest necroptosis induction (d). RIP1 co-IP. SK-LMS-1 ASS1low cells were treated with ADI-PEG20, chloroquine or both for 3 days. A significant RIP3 co-precipitation was observed upon exposure to 1 μg/ml ADI-PEG20 and 20 μM chloroquine, whereas caspase 8, which is negative regulator of ripoptosome formation, was reduced. Collectively, these observations are indicative of active ripoptosome formation and subsequent cell death executed preferentially by necroptosis