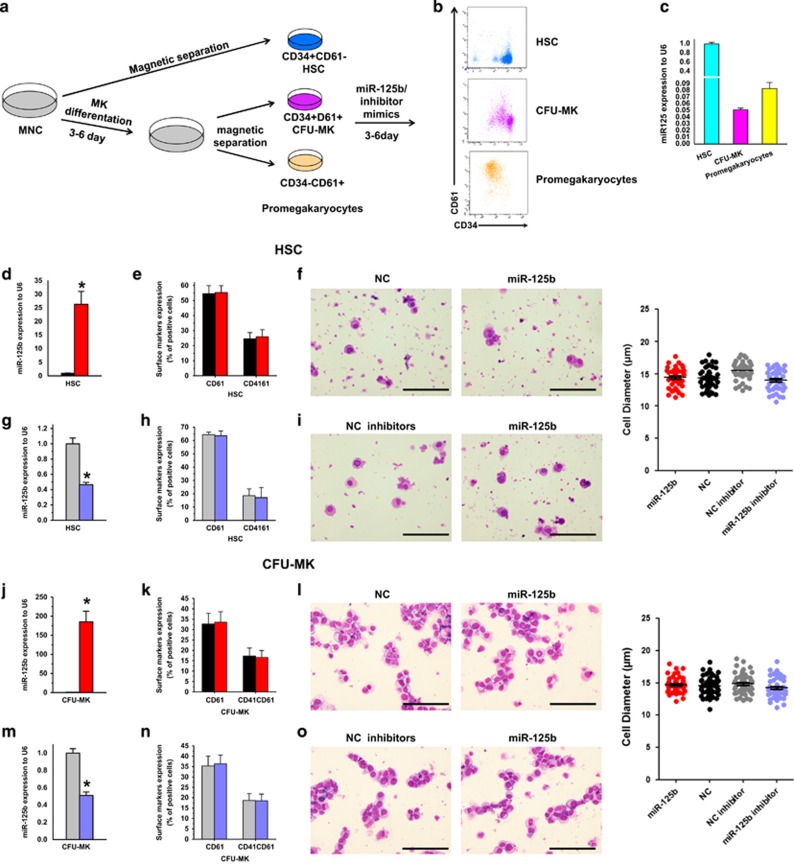
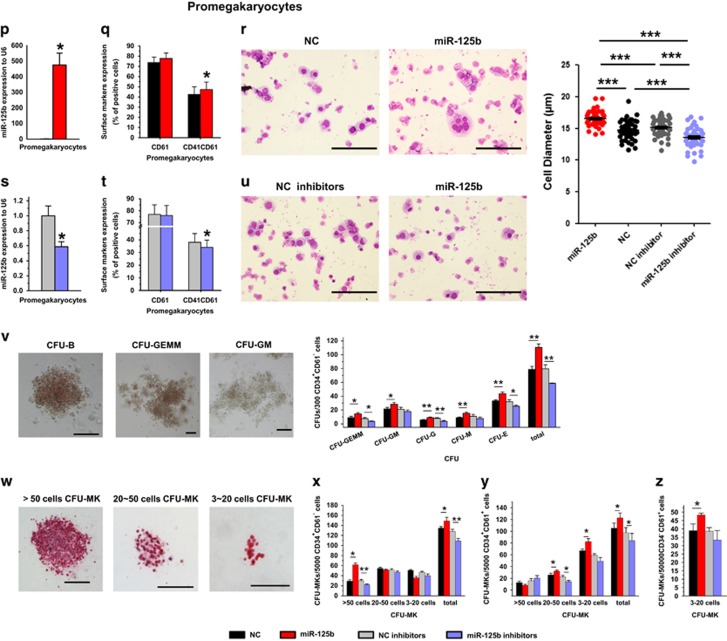
Figure 5.
Alteration of miR-125b in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, CFU-MK cells and pro-MKs have different effects on MK differentiation. (a) Schematic illustration of the experimental setup and the expression of differentiation markers during human megakaryocytic differentiation. (b) The expression of CD34 and CD61 on cells isolated by magnetic sorting, which represent different developmental stages of human MKs. (c) qPCR analysis of miR-125b expression at different stages of MK differentiation. (d, g, j, m, p and s) Relative miR-125b expression analyzed by qPCR. miR-125b expression is normalized to U6. (e, h, k, n, q and t) Altered expression of miR-125b influences the expression of MK integrins CD41 and CD61. (f, i, l, o, r and u) Altered expression of miR-125b impacts on megakaryocytic morphology and cell dimension. Cytospin-prepared MKs were stained with Wright–Giemsa solutions. Over 50 pro-MKs from five random views were measured. The error bars represent standard deviation (S.D.). Dunnett's test T3 were used for statistical analysis. (v) The typical morphology of CFU-E, CFU-GM, CFU-GEMM and quantification of CFUs with methylcellulose-based colony-forming assays of miR-125b, miR-125b inhibitor, NC and NC inhibitor-modified HSPCs. (w) Different size of CFU-MK colonies stained with human CD41 antibody. (x–z) Calculation of CFU-MKs with megacul colony-forming assays of miR-125b, miR-125b inhibitor, NC and NC inhibitors modification at different stages of human MK differentiation. Cells were obtained from four different donors and each sample was tested with three independent experiments for data presentation. All of the data are expressed as mean±S.D. Student's t-tests were used for statistical analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (scale bars: 100 μm)