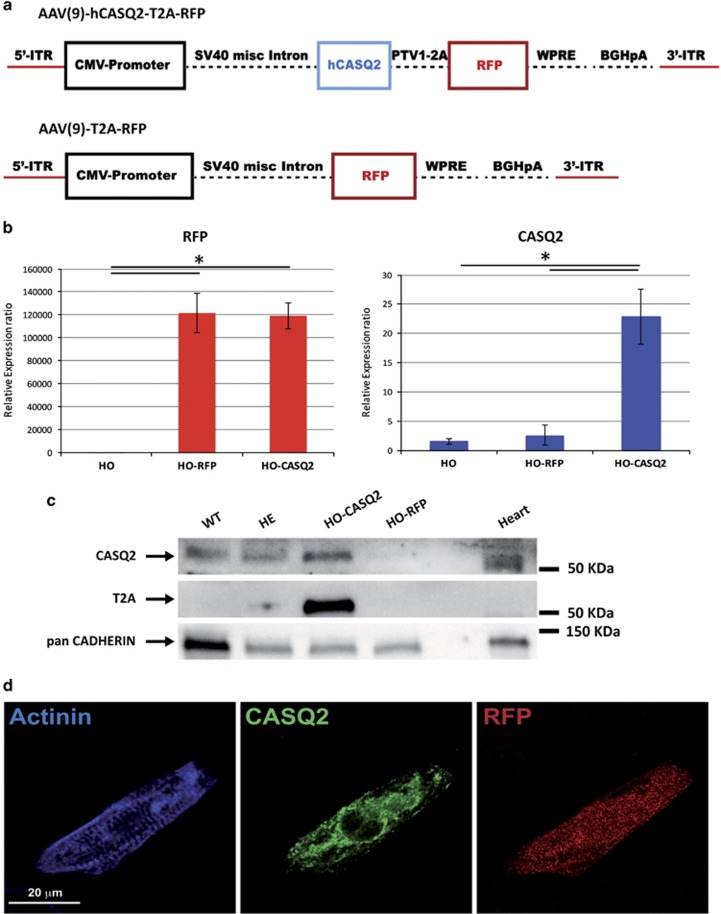
Figure 4.
AAV9-mediated administration of WT human CASQ2 gene re-establish physiological levels of calsequestrin-2 in HO-CMs. (a) Schematic representation of the adenoviral vectors (AAV9) carrying the WT human CASQ2 gene and the RFP marker (top) or the RFP alone (bottom), used for generation of the viral particle and for the gene therapy experiments. (b) Semiquantitative real-time PCR showing that the infection of CPVT-CMs with AAV9-WT-hCASQ2-T2A-RFP efficiently drives overexpression of CASQ2 gene and RFP in these cells (HO-CASQ2), while levels of CASQ2 in cells infected with AAV9-T2A-RFP (HO-RFP) were comparable to not infected CMs (HO). The data are relative to not infected CMs and were normalized to HGPRT expression. Values are mean±S.D.; *P<0.05. (c) western blot analysis showing re-expression of calsequestrin-2 in CPVT-CMs infected with AAV9-WT-hCASQ2 (HO-CASQ2). As expected, expression of the protein is not detectable in HO-CMs with the empty vector (HO-RFP), while the protein is present in CMs differentiated from both WT and HE iPSC lines. Protein extract from mouse heart has been used as positive control. T2A expression is instead detectable only in HO-CASQ2 CMs, indicating that the expression of the CASQ2 protein in those samples is the results of the viral-mediated gene delivery. (d) Immuno-staining for α-actinin and CASQ2 of HO-CMs infected with AAV9-WT-hCASQ2-T2A-RFP, showing positive expression of CASQ2 and positivity for RFP. Scale bar=20 μm