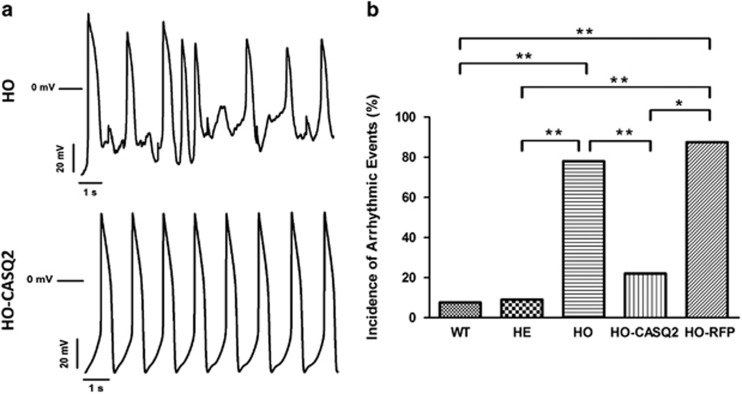
Figure 5.
AAV9-WT-hCASQ2 infection exerts an antiarrhythmic effect on CPVT2-iPSC-derived CMs. (a) Representative traces of spontaneous action potentials recorded in HO-CMs prior (HO, top) and after (HO-CASQ2, bottom) administration of AAV9-WT-hCASQ2 in the presence of a β-adrenergic stimulus (1 μM Iso). (b) Quantification of the incidence of Iso-induced DADs and TA, named as arrhythmic events (AE), in WT, HO, HO-CASQ2 (HO-CMs infected with the AAV9-hCASQ2-T2A-RFP vector), HO-RFP (HO-CMs infected with the empty vector) and HE CMs. (AEWT: 8%, 1 of 13 cells, AEHE: 9%, 2 of 22 cells; AEHO: 78%, 17 of 22 cells; AEHO-CASQ2: 22%, 2 of 9 cells; AEHO-RFP: 87.5%, 7 of 8 cells; *P<0.05, **P<0.01). The data have been generated on CMs differentiated from two independent clones from each subject