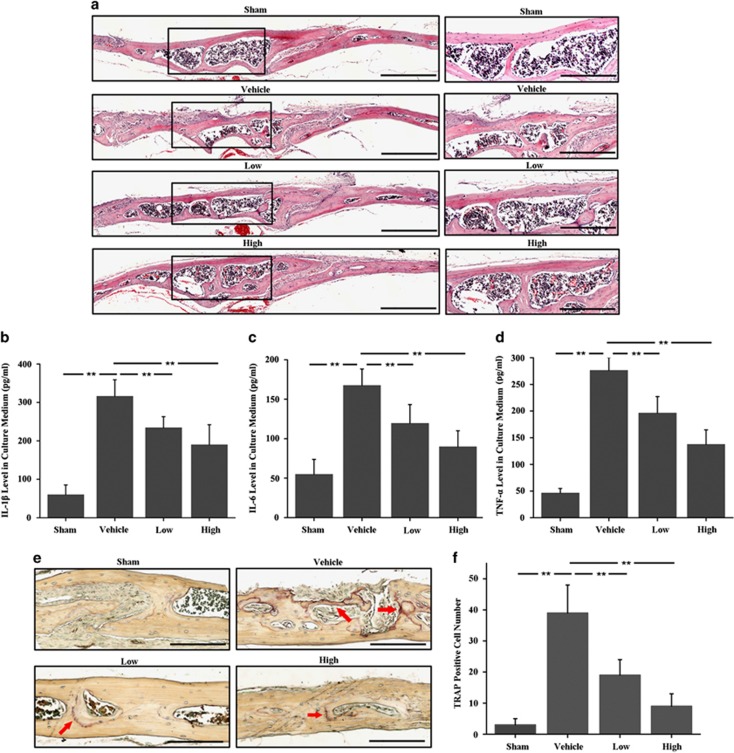
Figure 2.
The inhibitory effects of DFO on UHMWPE particles-induced mouse calvarial osteolysis were observed by histological and histomorphometric analysis. (a) H&E staining showed much more inflammatory reaction and prominent osteolysis in vehicle group compared with sham group, while the DFO-treated groups exhibited reduced inflammation and osteolysis. Scale bars, 500 μm. The rightmost pictures designate the larger magnification of the regions shown in inset. Scale bars, 300 μm. (b–d) The concentration of IL-1β (Figure 2b), IL-6 (Figure 2c) and TNF-α (Figure 2d) in the supernatant after 72 h of calvaria culture detected by ELISA. (e,f) TRAP staining showed that the number of osteoclasts lined along the eroded bone surface was significantly increased in UHMWPE particles group, which was obviously reduced in both low and high concentrations of DFO-treated groups. Red arrows indicated TRAP-positive cells. Low and high represent 10 and 30 mg/kg DFO application, respectively. Scale bars, 300 μm. n=6, **P<0.01