Fig. 7.
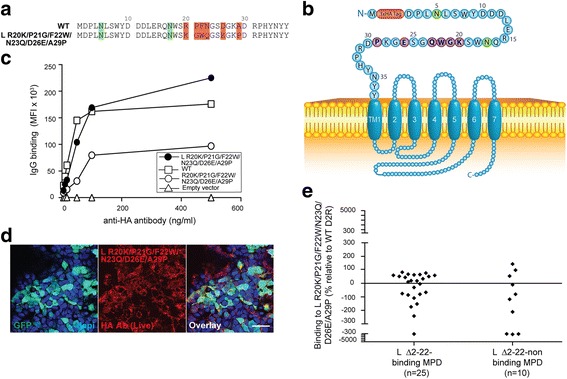
Extracellular N-terminal amino acids 20-22 contribute to a major binding region. a Amino acid sequences of extracellular 37 amino acids of R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P and WT D2R. Green = putative N-glycosylation sites; Red = amino acid changes. b Schematic of R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P at cell surface. Red = 3xHA tag; Green = N-glycosylation site; Blue = D2R sequence; Purple = point mutation. c Similar cell surface expression of L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P and WT D2R constructs was observed by flow cytometry on live cells, whereas R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P (without L signal peptide) has significantly decreased surface expression. No D2R expression from empty vector was observed. Representative data out of three independent experiments is shown. d Confocal images after live immunolabeling of L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P transfected HEK293 cells using an anti-HA antibody (scale bar = 50 μm). e Sera from anti-D2R antibody-positive movement and psychiatric disorders (MPD) that bind L Δ2-22 (n = 25) or not (n = 10) were incubated with empty vector-, WT D2R-, and L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P-transfected live HEK293 cells at 1:50 dilution, followed by AF647-conjugated anti-human IgG secondary antibody, and flow cytometry analysis. Percentage of sera binding to L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P (MFI %) was calculated using the formula described in Material and Methods. Among the group that bound L Δ2-22, 56% patients (14/25) recognized L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P, whereas 44% (11/25) showed no immunoreactivity to the mutant. Among the group that did not bind L Δ2-22, 7/10 (70%) did not recognize L R20K/P21G/F22W/N23Q/D26E/A29P mutant, whereas 3/10 (30%) did bind to it. Binding threshold is represented by solid line on graph. Representative data out of three experiments is shown
