Fig. 9.
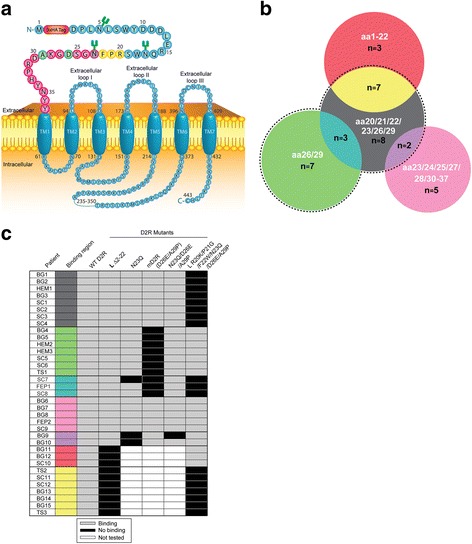
Major binding regions of human anti-D2R antibody on D2R extracellular N-terminus. a Schematic of human D2R and extracellular N-terminal amino acids of D2R involved in antibody binding. MPD patient antibody binding was dependent on binding regions centered on residues at positions 20 to 22 (yellow), 26 and 29 (green), and 23 to 37 (magenta). b Venn diagram of the main binding regions of 35 pediatric patient sera on human D2R extracellular N-terminus. The black dotted line shown represents binding to residues 20 to 29 by the majority of sera (77%, 27/35). Binding to R20, P21, and F22 is shown in yellow (26%, 7/27), and cyan and green groups represent immunoreactivity to D26 and A29 (37%, 10/27). Seven sera bound to residues 23 to 37 (binding to L Δ2-22 D2R) excluding D26 and A29 (magenta and purple), among which two were dependent on N-glycosylation at N23 (purple). Indeed, the magenta group bound to all D2R mutants modified at R20, P21, F22, N23, D26, and A29, suggesting binding outside these residues. Red shows binding to residues 1 to 19 (9%, 3/35). The Venn diagram was compiled with data summarizing three independent experiments illustrated by black and gray boxes shown in panel c. Amino acids (aa) bound by patient sera are shown in white text. c Table of binding patterns of 35 individual anti-D2R antibody-positive patient sera according to D2R mutants (columns) and clinical disorders (rows). Light gray boxes represent binding to mutant and black boxes represent no binding. 10/35 patient sera did not bind to residues 23-37 (L Δ2-22 D2R), and therefore were not tested on mutants encompassing these amino acids (white boxes). No clinical phenotype could be associated with a specific binding pattern. SC, Sydenham chorea; BG, basal ganglia encephalitis; HEM, Post-herpes simplex virus encephalitis autoimmune movement disorder; TS, Tourette syndrome; FEP, first episode psychosis. Colored boxes relate to Venn diagram in panel b
