Figure 3.
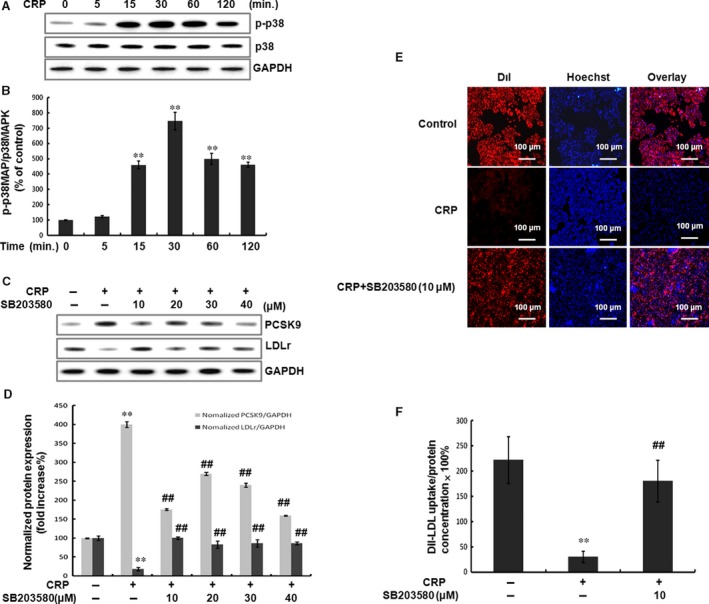
CRP‐induced PCSK9 expression and LDL uptake through p38MAPK pathway in HepG2 cells. (A) (B) CRP induced activation of signal transduction. Western blot analyses showed the effect of CRP (10 μg/ml) on p38MAPK phosphorylation and p38MAPK expression at 5, 15, 30, 60, 120 min. (C) (D) CRP induced the up‐regulation of PCSK9 but the down‐regulation of LDLR was inhibited by the p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, in HepG2 cells. After serum‐starvation overnight, the cells were pre‐treated with SB203580 (10, 20, 30 and 40 μM) for 1 hr and then stimulated with 10 μg/ml CRP for 24 hrs. The extracted protein samples were analysed by Western blot. (E) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of cell‐associated Dil‐LDL (red), Hoechst‐stained nuclei (blue) and the overlay. (F) Fluorescence of isopropanol‐extracted Dil (520–570 nm, normalized to the cell protein). Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). Significance: **P < 0.01 versus control; ## P < 0.01 versus the CRP‐treated group. CRP, C‐reactive protein; PCSK9, pro‐protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; LDLR, low‐density lipoprotein receptor.
