Figure 1. Biological schematic diagram of the Signalling Model Example .
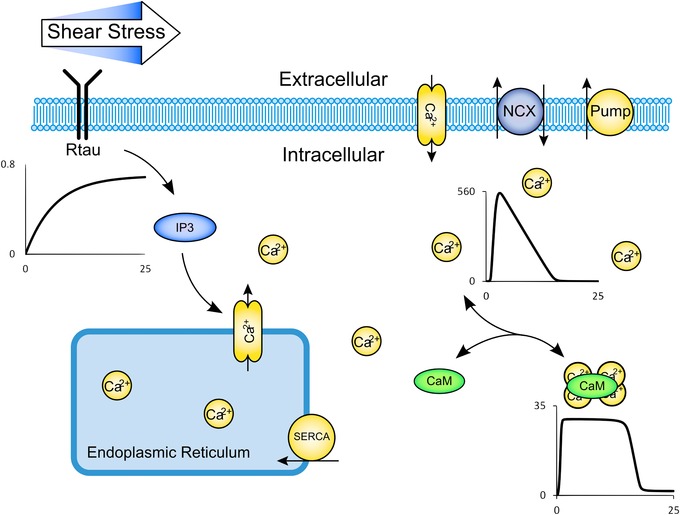
Shear stress sensed by receptors (Rtau) leads to IP3 production and store calcium release. Calcium is also transferred between the extra‐ and intracellular compartments via stress‐sensitive calcium channels, calcium/sodium exchanger, a calcium pump, a basal calcium leak and capacitative calcium entry. Calcium leads to activation of calmodulin (CaM). Representative traces of Rtau, free intracellular calcium, and activated calmodulin over a 25 s simulated time period are shown (please see the Supporting information for more details on the traces).
