Figure 1.
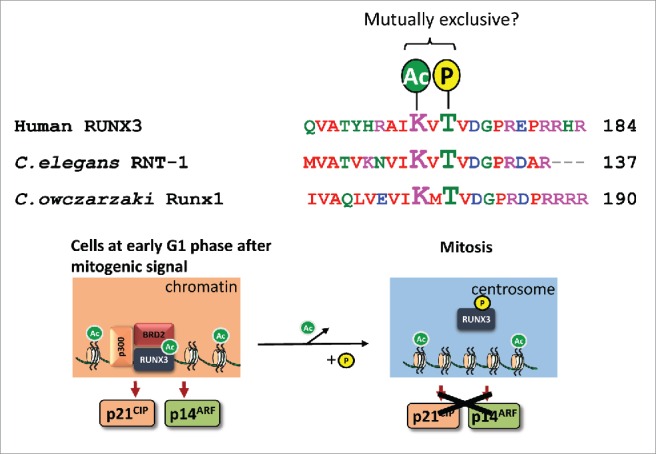
Proposed model for crosstalk between post-translational modifications of the highly conserved T173 and K171 residues Top, alignment of human RUNX3 with RUNX proteins from Caenorhabditis elegans and Capsaspora owczarzaki. Bottom, upon mitogenic stimulation, p300 mediates acetylation of RUNX3; acetylated RUNX3 binds to BRD2 to activate p21WAF1(CIP and p14ARF transcription during early stages of G1 phase – this is a key cellular mechanism to safeguard against persistent mitogenic signals6. As the cell cycle progresses, we propose that deacetylation of K171 results in cessation of p21WAF1(CIP and p14ARF transcription in S phase, and permits T173 phosphorylation during G2/M transition – the phosphorylated RUNX3 is released from DNA and subsequently localizes to the centrosome to license mitotic entry.
