Figure 1.
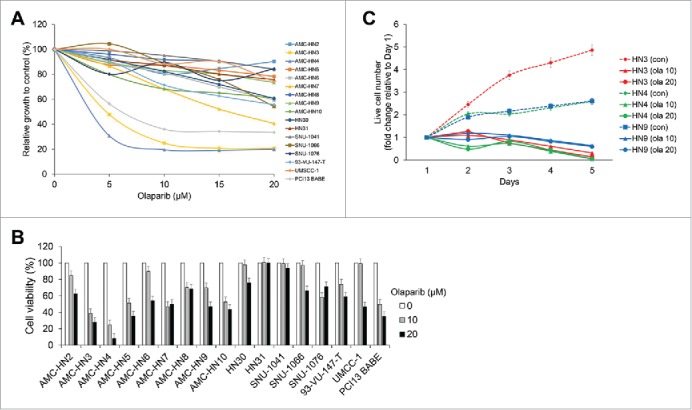
Olaparib selectively inhibits some head and neck cancer (HNC) cell lines. The cytotoxic effects of olaparib were evaluated in cultured human HNC cells. (A) A few HNC cell lines, including AMC-HN3, -HN4, and PCI13 BABE, demonstrated marked decreases in survival in a MTT assay. (B) In a trypan blue exclusion assay, cell viability was reduced by more than 50% in AMC-HN5 and -HN7 cells at a 10-μM concentration of olaparib. (C) Live cell numbers at the indicated time points, expressed as relative values to the cell counts on day 1, were compared (con, control; ola 10 and 20, each olaparib 10 and 20 μM), revealing that the effects of olaparib on HNC cell growth were more likely cytostatic than cytotoxic. Error bars indicate standard errors.
