Figure 1.
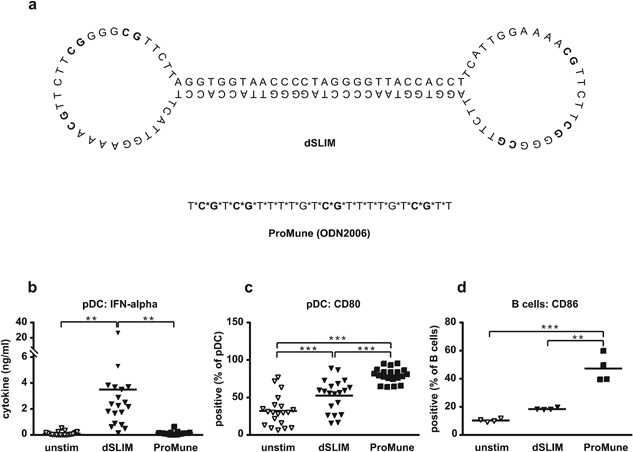
Structure and functions of dSLIM® and ProMune® on TLR9 positive cells. (a) Sequences and proposed structures of dSLIM® and ProMune®. CG‐motifs are depicted in bold. *Indicate a PTO bond instead of genuine phosphodiester bond between deoxynucleotides. (b–d) Isolated TLR9‐positive cells, pDC, and B cells, were treated with dSLIM® or ProMune® at final concentrations of 3 μM or medium alone for 48 h. A final concentration of 10 ng/mL IL‐3 was added to the pDC cultures. IFN‐α levels in the supernatants of pDC (b) were determined by a bead‐based multiplex immunoassay (n = 19, means are shown, **P < 0.01, repeated measures ANOVA, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test). pDC were stained with αCD80 antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry (c). Frequency of CD80‐expressing cells within the pDC population are shown (n = 20, means are shown, ***P < 0.001, repeated measures ANOVA, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test). B cells (d) were stained with αCD86 antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. Frequency of CD86‐expressing cells within the B cell population are shown (n = 4, means are shown, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, repeated measures ANOVA, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test).
