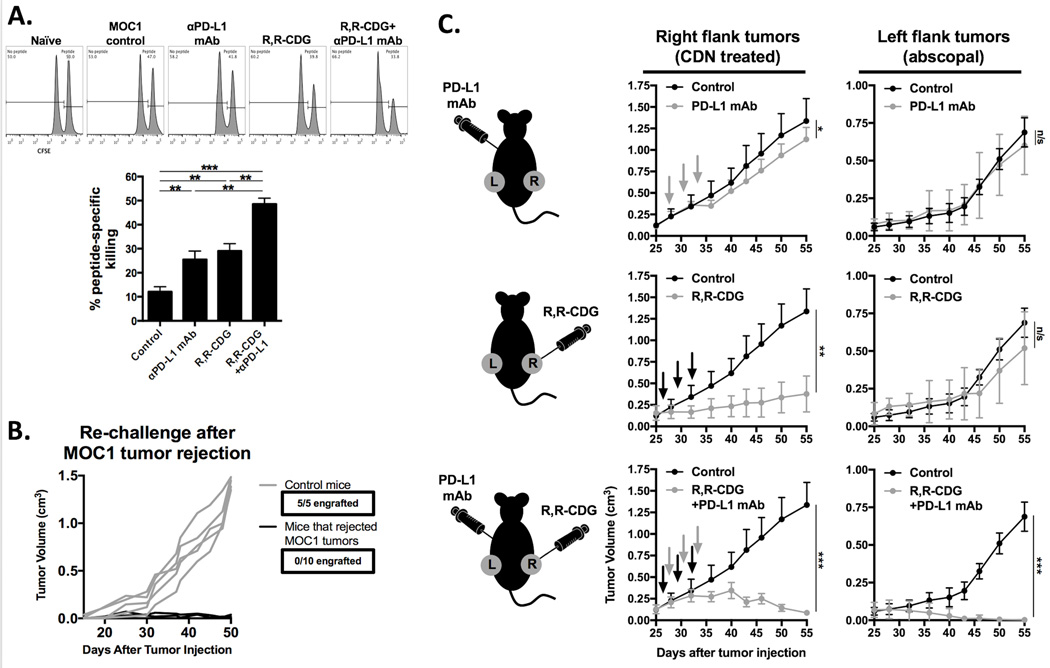
Figure 7. Combination CDN and PD-L1 mAb treatment induces immunologic memory, protection against challenge and abscopal tumor control.
A, CFSE-based in vivo CTL analysis using p15E604–611 (KSPWFTTL) as a model antigen (n = 3 mice/group). Mice from the combination R,R-CDG and PD-L1 mAb group rejected their tumors, mice from all other groups did not reject tumors. Representative histograms from each cohort are displayed. p15E peptide-specific cell killing was quantified relative to naïve, non-tumor bearing WT B6 mice (bar graph). B, WT B6 mice or mice that rejected established MOC1 tumors following combination CDN and PD-L1 mAb treatment were challenged with 2×106 MOC1 cells. C, 2×106 MOC1 cells were injected bilaterally in WT B6 mice. Once tumors were stablished (0.1 cm3), mice were treated with CDN (right flank tumors only) and systemic PD-L1 mAb alone or in combination (n = 5 mice/group) and both right and left flank tumors were followed for tumor growth. Black arrows are R,R-CDG treatment, grey arrows are PD-L1 mAb treatment. *, P < 0.05; **; P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ANOVA. n/s, not significant.