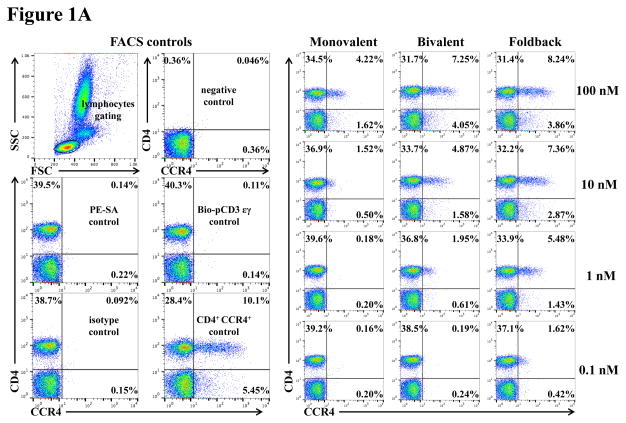
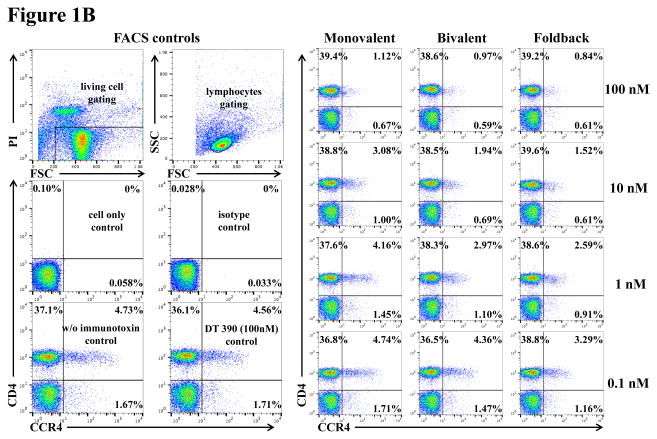
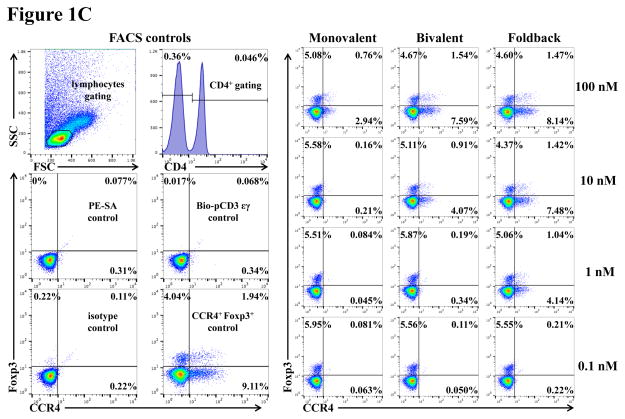
Fig. 1.
In vitro binding and depletion analysis of the anti-human CCR4 immunotoxins to porcine CCR4+ blood cells or PBMC. A) Flow cytometry binding analysis of the anti-human CCR4 immunotoxins to CCR4+ cells within porcine whole blood. Monovalent: monovalent anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin [DT390-scFv (1567)]; Bivalent: bivalent anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin [DT390-BiscFv (1567)]; Foldback: single-chain foldback diabody anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin; PE-SA: PE-conjugated streptavidin; Bio-pCD3εγ: Biotin-labeled porcine CD3εγ. B) In vitro depletion of the CCR4+ cells within porcine PBMC using the anti-human CCR4 immunotoxins. C) Flow cytometry binding analysis of the anti-human CCR4 immunotoxins to the Foxp3+CCR4+ porcine PBMC. Fig. 1C analysis was CD4 gated. All of the data (Fig. 1A–C) are representative of three experiments with blood samples from three different animals. The variance data of Fig. 1A–C is included in the supplement table 1.