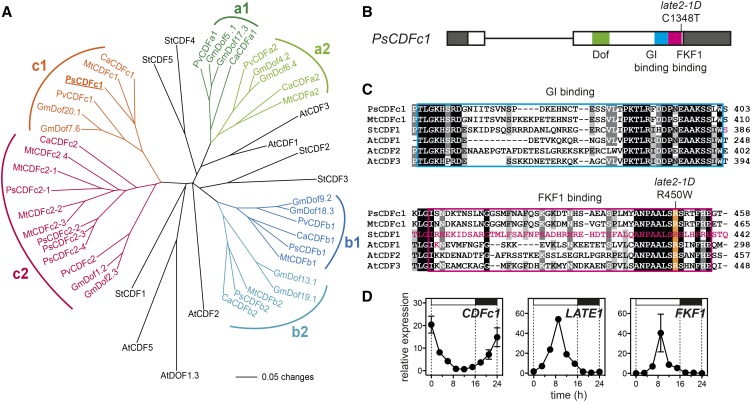
Figure 5.
The late2-1D Mutant Carries a Mutation in a CDF Homolog.
(A) Phylogram of the legume CDF family with reference to CDF genes from Arabidopsis and potato. Branches with bootstrap values <55% obtained from 1000 trees have been collapsed. The analysis is based on the sequence alignment shown in Supplemental File 1. Sequence details are given in Supplemental Table 1.
(B) Diagram of the pea CDFc1 gene showing the nature and location of the mutation in late2-1D in the FKF1 binding domain. Exons are shown as boxes, with coding sequence in white and untranslated regions in dark gray. Functional domains are indicated.
(C) Alignment of pea CDFc1 and other CDF homologs showing conserved residues in the GI binding (blue box) and FKF1 binding (pink box) domains. The arginine affected by the late2-1D mutation is highlighted in orange. The residues deleted in the naturally occurring potato StCDF1.2 and 1.3 variants, and altered in the Arabidopsis AtCDF1 K253A variant, all of which affect FKF1 binding (Imaizumi et al., 2005; Kloosterman et al., 2013), are indicated in pink. Shading indicates degree of conservation (black = 100%, dark gray = 80%, and light gray = 60%).
(D) Comparison of rhythmic expression patterns for CDFc1, LATE1, and PsFKF1 under LD conditions. Transcript levels were determined in the uppermost fully expanded leaf of 3-week-old wild-type (NGB5839) plants grown under a 16-h photoperiod at 20°C. Mean values ± se are shown for n = 2 biological replicates, each consisting of pooled material from two plants. Day and night periods are indicated by white and black bars, respectively, above the graph.
At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Ca, Cicer arietinum; Gm, Glycine max; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Ps, Pisum sativum; Pv, Phaseolus vulgaris; St, Solanum tuberosum.