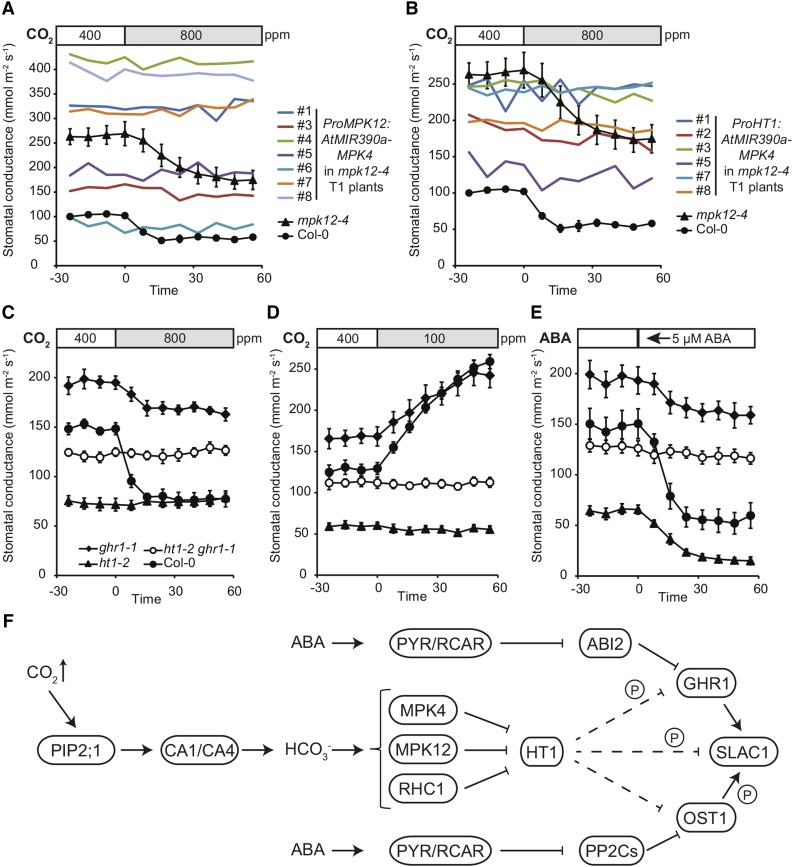
Figure 7.
MPK4 Silencing in Guard Cells Abolishes CO2-Induced Stomatal Closure.
ht1-2 ghr1-1 double mutant is CO2 and ABA insensitive and has wild-type-like stomatal conductance.
(A) and (B) Stomatal response to increase in CO2 concentration (from 400 to 800 ppm) of intact mpk12-4 T1 plants transformed with ProMPK12:AtMIR390a-MPK4 or ProHT1:AtMIR390a-MPK4, respectively. Results from one experiment with several independent transgenic plants marked with numbers are shown. For Col-0 and mpk12-4, and error bars mark se (n = 4 and n = 6, respectively), and data from the same experimental series are presented in (A) and (B).
(C) to (E) Stomatal response of intact plants to increase in CO2 concentration (from 400 to 800 ppm), reduction in CO2 concentration (from 400 to 100 ppm), and 5 µM ABA, respectively. Stimulus was applied at time point zero, the experiment was repeated three times, and representative results from one experiment are shown. Error bars indicate se (n = 5).
(F) Model for the role of HT1, MPK12/MPK4, and GHR1 in the regulation of SLAC1 activation in CO2-induced stomatal closure. PIP2 aquaporins facilitate CO2 influx into guard cells. The PIP2;1-interacting carbonic anhydrase CA4 (Wang et al., 2016) together with CA1 accelerate CO2/bicarbonate signal transduction. MPK12/MPK4 and RHC1 form a double negative regulation chain with HT1, controlling GHR1 and then SLAC1 activation in response to CO2. CO2 activates MPK4/MPK12 and RHC1, which then inhibit HT1; thus, HT1 no longer inhibits SLAC1 activation by GHR1, resulting in stomatal closure in response to increased CO2 concentration. Direct HT1-induced inhibition of SLAC1 has not yet been excluded and its contribution would need to be characterized. HT1 can phosphorylate GHR1 and SLAC1. CO2 and ABA-signaling pathways converge at the level of GHR1 kinase, which can be regulated by ABI2, whereas OST1 is regulated by several PP2Cs (ABI, ABI2, PP2CA, and HAB1).