Figure 5. Podocarpic acid (PA) is a TRPA-1 agonist and SKN-1 activator that ameliorates pathogenic phenotypes of C. elegans glod-4.
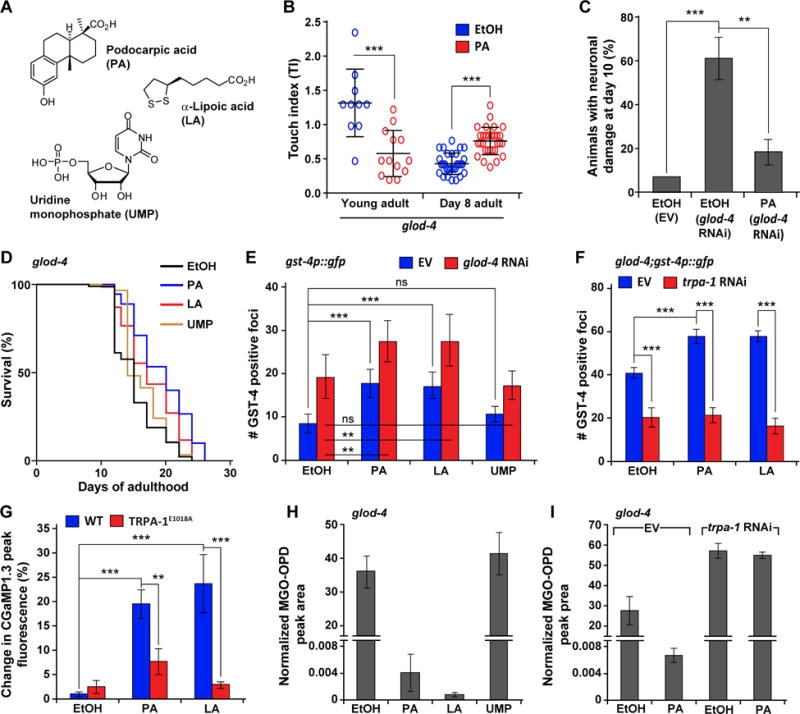
(A) Structures of podocarpic acid (PA), α-lipoic acid (LA), and uridine monophosphate (UMP).
(B)Touch indices in glod-4, supplemented with EtOH (control) or PA (20 μM) during young adult stage or day 8 of adulthood.
(C) Neuronal damage in pan-neuronal GFP animals (unc-33p∷gfp) at day 10 of adulthood, reared on empty vector (EV, L4440) or glod-4 RNAi, supplemented with EtOH (control) or PA (20 μM). n = 45.
(D) Survival curves for glod-4 mutant animals supplemented with EtOH (control), PA, LA, or UMP (20 μM).
(E) Quantification of GFP foci in gst-4p∷gfp animals reared on EV or glod-4 RNAi, supplemented with EtOH (control), PA, LA, or UMP (20 μM). n = 10.
(F) Quantification of GFP foci in glod-4;gst-4p∷gfp animals reared on EV or trpa-1 RNAi, supplemented with EtOH (control), PA or LA (20 μM). n = 15.
(G) Percentage change in peak fluorescence intensity observed in transgenic animals expressing intestinal GCaMP1.3 (Ca2+ sensor) and a wild-type TRPA-1 or TRPA-1E1018A (Ca2+ impermeable) mutant channel, in response to EtOH (control), PA or LA (20 μM). n = 10.
Levels of MGO in
(H) glod-4, supplemented with EtOH (control), PA, LA, or UMP (20 μM) or in
(I) glod-4, reared on EV or trpa-1 RNAi, supplemented with EtOH (control) or PA.
Data are represented as mean ± SD. Significance: *P<0.05, **P<0.005 and ***P<0.0005.
