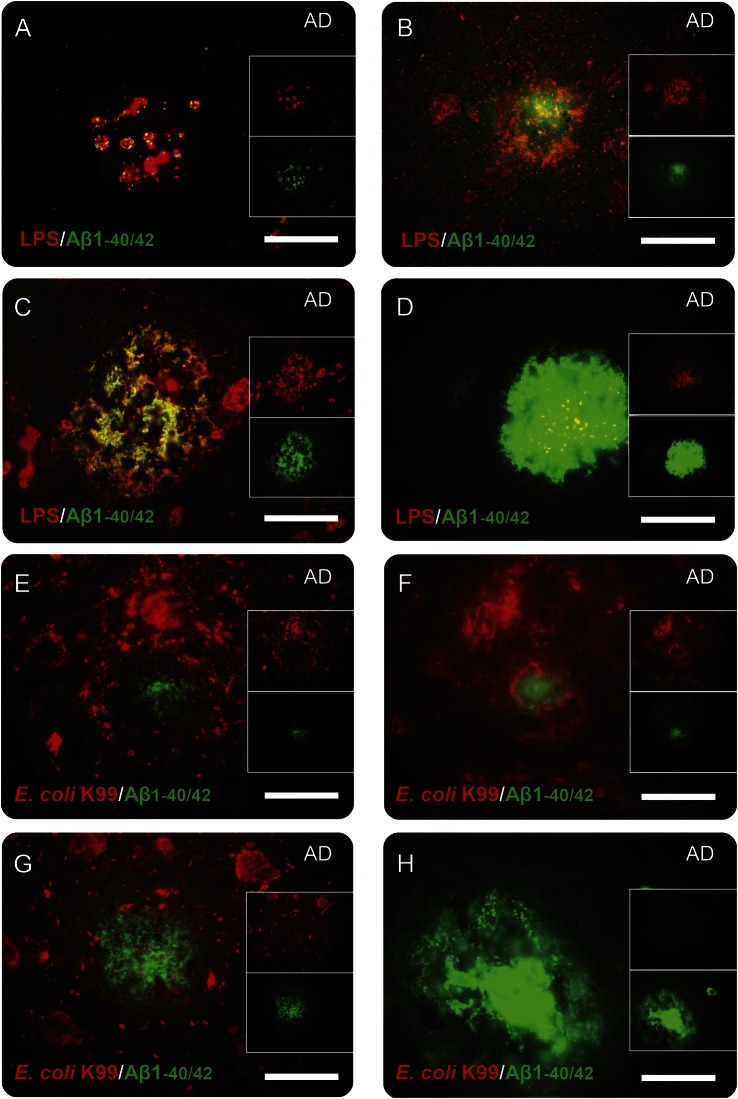
Figure 4. Association of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and Escherichia coli K99 pili protein with amyloid plaques in Alzheimer disease (AD) brains.
There were several different patterns of colocalization of LPS and Aβ1-40/42 in AD brains. There were clusters of predominantly LPS particles that colocalized with Aβ1-40/42 (A). There were Aβ1-40/42 deposits that colocalized with LPS and were surrounded by LPS (B, C). Finally, there were confluent Aβ1-40/42-stained amyloid plaques that had scattered LPS particles within them (D). These LPS results contrasted with E coli K99 pili protein, which often surrounded small Aβ1-40/42-stained amyloid plaques (E–G). For larger amyloid plaques (diameter >50 μm), E coli K99 was usually absent (H). Bar = 25 μm.