Abstract
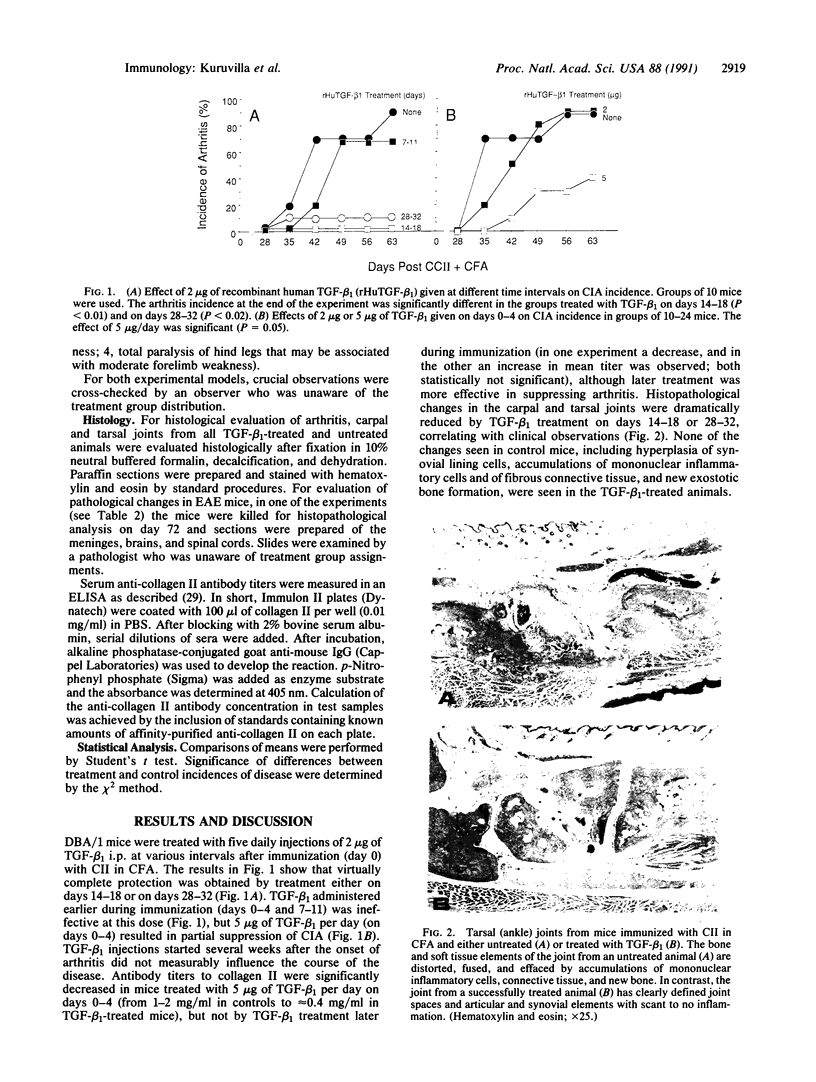
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor alpha are thought to contribute to the inflammatory response associated with autoimmune diseases. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) counteracts many effects of these cytokines and has various immunosuppressive properties. In the present study, it is shown that microgram amounts of TGF-beta 1, injected daily for 1-2 weeks, protect against collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (REAE), the animal models for rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, respectively. When administered during induction of the disease, TGF-beta 1 prevents CIA but only delays the onset of REAE by 2-3 days. However, when administered during a remission. TGF-beta 1 prevents the occurrence of relapses in REAE. The results suggest that TGF-beta 1 has powerful anti-inflammatory effects, mimicking in some respects the beneficial effects of immunosuppressive drugs in these experimental models of autoimmune disease, but without discernable adverse effects.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Welgus H. G., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1694–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Chronologic neuropathology of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):171–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantry D., Turner M., Abney E., Feldmann M. Modulation of cytokine production by transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4295–4300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer M. A., Hernandez A. D., Townes A. S., Stuart J. M., Kang A. H. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats: antigen-specific suppression of arthritis and immunity by intravenously injected native type II collagen. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2995–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Chiu H. H., Wong G. H., McCabe S. M., Palladino M. A. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates the expression of class II histocompatibility antigens on human cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C. M., Ruscetti F. W., Palaszynski E. W., Falk L. A., Oppenheim J. J., Keller J. R. Transforming growth factor beta is a potent inhibitor of interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor expression: proposed mechanism of inhibition of IL-1 action. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):737–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha reciprocally regulate the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Comparison between natural porcine platelet-derived TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2, and recombinant human TGF-beta 1. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2312–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Figari I. S., Shalaby M. R., Lackides G. A., Lewis G. D., Shepard H. M., Palladino M. A., Jr Inhibition of cytokine production by cyclosporin A and transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):571–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Miyamoto T., Nishioka K., Okumura K. Selective loss of suppressor T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients: analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes by 2-dimensional flow cytometry. J Rheumatol. 1986 Oct;13(5):853–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Bendele A. M., Carlson D. G. In vivo administration with IL-1 accelerates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins S. J., Meager A. Cytokines in synovial fluid: II. The presence of tumour necrosis factor and interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):88–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Kitaura M., Kato T., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Muramatsu S. Contrasting effect of alpha/beta- and gamma-interferons on expression of macrophage Ia antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1030–1035. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamura N., Hashimoto M., Nakahara K., Aoki H., Yamaguchi I., Kohsaka M. Immunosuppressive effect of FK506 on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jan;46(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamura N., Hashimoto M., Nakahara K., Nakajima Y., Nishio M., Aoki H., Yamaguchi I., Kohsaka M. Immunosuppressive effect of FK506 on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1988;10(8):991–995. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(88)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Salazar A. M., Herndon R., Reese P. A., Freeman A., Jozefowicz R., Cuetter A., Husain F., Smith W. A., Ekes R. Intrathecally administered natural human fibroblast interferon reduces exacerbations of multiple sclerosis. Results of a multicenter, double-blind study. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jun;44(6):589–595. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520180013008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibara N., Hotokebuchi T., Takagishi K., Katsuki I. Paradoxical effects of cyclosporin A on collagen arthritis in rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2007–2015. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Jakowlew S., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Transforming growth factor beta is an important immunomodulatory protein for human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3855–3860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Taylor A. S., Delsing G. A., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Further studies of the role of transforming growth factor-beta in human B cell function. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1868–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Panitch H. S., Braheny S. L., Sipe J. C., Rice G. P., Huddlestone J. R., Francis G. S., Hooper C. K., Kamin-Lewis R. M., Johnson K. P. Systemic alpha-interferon therapy of multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1984 Oct;34(10):1273–1279. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.10.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad S., Klareskog L., Hedfors E., Forsum U., Sundström C. Phenotypic characterization of synovial tissue cells in situ in different types of synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Nov;26(11):1321–1332. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Warren M. K., Vogel S. N. Antagonistic effect of interferon-beta on the interferon-gamma-induced expression of Ia antigen in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1857–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee I. A., Antoni F. A., Mason D. W. Spontaneous recovery of rats from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is dependent on regulation of the immune system by endogenous adrenal corticosteroids. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):431–445. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa H., Takenaka A., Itoyama Y., Mori R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. A model of predictable relapse by cyclophosphamide. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Apr;78(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L., Letvin N. L., Hagan M., Daley J., Schlossman S. F. Selective loss of the suppressor-inducer T-cell subset in progressive multiple sclerosis. Analysis with anti-2H4 monoclonal antibody. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 8;316(2):67–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701083160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., Bober L. A., Robinson M. E., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Suppression of type II collagen-induced arthritis by intragastric administration of soluble type II collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7443–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha A., Toscas A., Jensen M. A. Interferon beta augments suppressor cell function in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):207–210. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Drobish D. G. Cyclophosphamide: effect on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. Science. 1969 Jul 11;165(3889):191–192. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3889.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phadke K., Fouts R. L., Parrish J. E., Butler L. D. Evaluation of the effects of various anti-arthritic drugs on type II collagen-induced mouse arthritis model. Immunopharmacology. 1985 Aug;10(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(85)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quere P., Thorbecke G. J. Multiple suppressive effects of transforming growth factor beta 1 on the immune response in chickens. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):468–477. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90221-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Figari I. S., Espevik T., Palladino M. A., Jr Inhibition of cytotoxic T cell development by transforming growth factor beta and reversal by recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):991–998. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow H. J. BSC-1 growth inhibitor/type beta transforming growth factor is a strong inhibitor of thymocyte proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5531–5533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Burlington D. B., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Effects of transforming growth factor beta on the functions of natural killer cells: depressed cytolytic activity and blunting of interferon responsiveness. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3916–3920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Ammann A. J. Suppression of immune cell function in vitro by recombinant human transforming growth factor-beta. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore A., Jaglal S., Keystone E. C. Enhanced interleukin 1 generation by monocytes in vitro is temporally linked to an early event in the onset or exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):293–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda A. E., Birnbaum J. E., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Studies on type II collagen-induced polyarthritis in rats. Effect of antiinflammatory and antirheumatic agents. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Apr;24(4):616–624. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Blanchette B. W., Bhan A. K., Colvin R. B. The immunopathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. I. Quantitative analysis of inflammatory cells in situ. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2393–2401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub C., Zubler R. H. Immortalization of EBV-infected B cells is not influenced by exogenous signals acting on B cell proliferation. Effects of mutant EL-4 thymoma cells and transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagishi K., Kaibara N., Hotokebuchi T., Arita C., Morinaga M., Arai K. Effects of cyclosporin on collagen induced arthritis in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Apr;45(4):339–344. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.4.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E. Rheumatologic therapy for the 1990s. Evolution or revolution? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Aug;15(3):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunawaki S., Sporn M., Ding A., Nathan C. Deactivation of macrophages by transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):260–262. doi: 10.1038/334260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W. D., Firestein G. S., Taetle R., Kaushansky K., Zvaifler N. J. Cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. II. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in rheumatoid synovial effusions. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):876–882. doi: 10.1172/JCI113971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]