Figure 3.
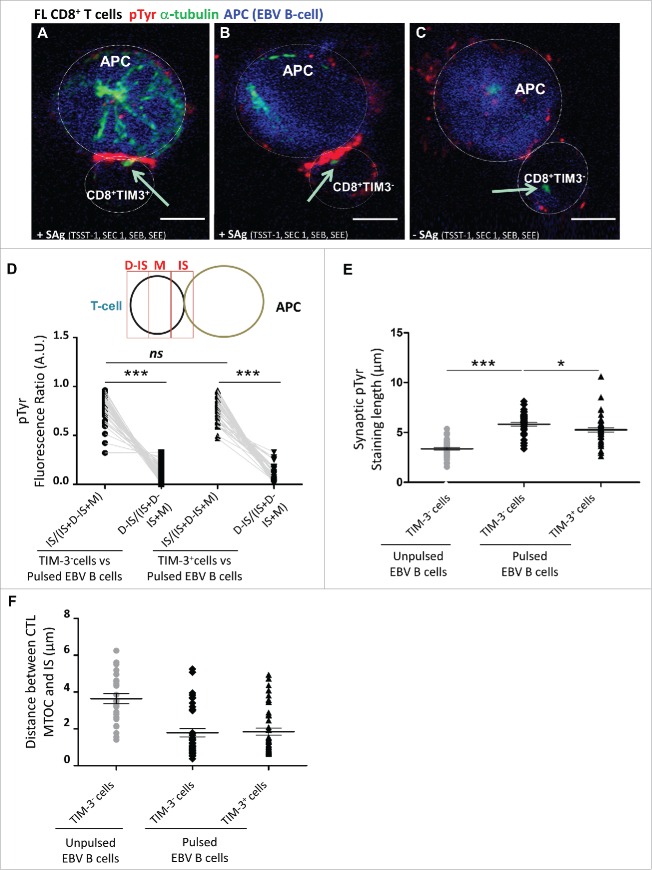
Minor alteration of immunological synapse formation in CD8+TIM-3+ T cells from FL lymph nodes. Representative IS formation between CD8+TIM–3+ T cells (A) and CD8+TIM-3– T cells (B and C) from FL lymph nodes (n = 3) stained with α-tubulin (green) and pTyr (red) after 15 min conjugation with unpulsed (C) or SAg-pulsed (A and B) EBV B cells (blue stained). The yellow arrow indicates the MTOC position. Bar 5 µm. (D) Scheme depicting pTyr intensity measurement defined by three reference areas at different regions of the T cell surface: immunological synapse between T cell and target B cell (=IS), distal synapse region (=D–IS) and area between these two regions (=M). The intensity of pTyr red fluorescence was measured in the different cell areas as indicated in the scheme. Fluorescence intensity in the regions of interest was compared to that of the entire cells using the Metamorph® software. In particular, the mean intensity of pTyr red fluorescence in CD8+TIM-3– and in CD8+TIM3+ T cells was calculated by dividing the pTyr red pixels in IS and those in the D-IS for the total red pixel of entire cell (IS+M+D-IS) (E). Comparison of pTyr staining lenght at the IS area between pulsed CD8+TIM-3+ T cells and CD8+TIM-3– T cells (unpulsed CD8+TIM-3– T cells as negative control) (µm). (F) Comparison of the distance between microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) and the center of the IS area between pulsed CD8+TIM-3+ T cells and CD8+TIM-3– T cells (µm). Each dot in Fig. 3D–F represents a cell. Data are from three FL patients. For the different FL samples standardized conditions for pinhole size, for gain and offset (brightness and contrast), were used for image capture. Wilcoxon signed-rank test using the GraphPad Prism software (version 6; GraphPad) was used to determine the statistical significance of differences between the groups. p = 0.3699, p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001, respectively (D); p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0232, respectively (E).