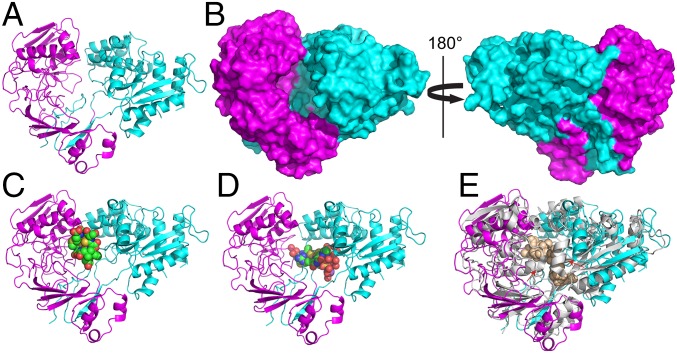
Fig. 5.
The 1.9-Å resolution crystal structure of Mc. parvus OBBP apo MbnE. (A) Cartoon representation with the two domains colored in magenta and cyan. (B) Surface representations of the structure show a cavity at the domain–domain interface that measures ∼15 Å across and 30 Å high. The cavity is open only to one side, consistent with it being the only entry point for the substrate. Docking models generated with the structures of CuMbns from Ms. trichosporium OB3b (C) and Mc. sp. M (D) reveal that the cavity can accommodate both forms of CuMbns. (E) Superposition of the Mc. parvus OBBP MbnE structure with that of nonapeptide-bound AppA from B. subtilis (PDB 1XOC). Major structural rearrangements include the ordering of a loop in the N-terminal domain and the movement of a α-helix closer to the domain–domain interface (red arrows).