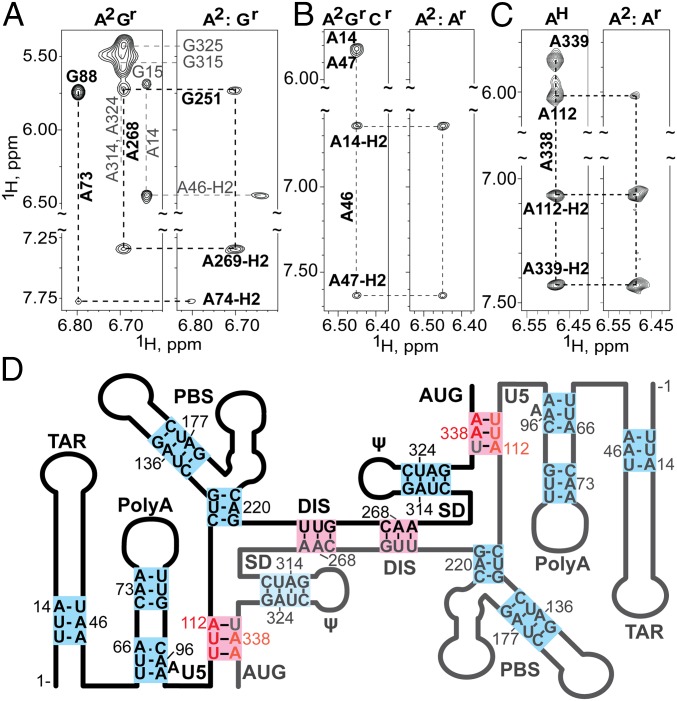
Fig. 3.
(A–C) Portions of 2D NOESY spectra obtained for mixed, differentially 2H-labeled 5′-L344 RNAs that probe the DIS and PolyA helices (NOEs that differentiate inter- or intramolecular base pairing are denoted with black labels and thick lines; noninformative NOEs are labeled gray). (A) Spectra obtained for A2Gr (Left) and mixed A2:Gr 5′-L344 (Right) samples. The A268-H2 to G251-H1′ NOE observed for the mixed sample is indicative of intermolecular base pairing at DIS (see also Fig. 2C). In contrast, the absence of an A73-H2 to G88-H1′ in the mixed sample indicates that base pairing in the PolyA helix is intramolecular. (B) Regions of spectra obtained for A2GrCr and A2:Ar 5′-L344 samples that probe TAR. Absence of an A46-H2 to A14-H1′ cross-strand NOE for the mixed sample is indicative of intramolecular base pairing. (C) Spectra obtained for AH and mixed A2:Ar-labeled 5′-L344-UUA samples that probe the U5:AUG helix. The cross-strand NOE from A338-H2 to A112-H1′ observed for the mixed sample reveals that U5:AUG base pairing is intermolecular. (D) Secondary structure consistent with the combined NMR probing data, in which the TAR, PolyA, PBS, and ψ helices are formed by intramolecular base pairs (blue) and the U5:AUG and DIS helices comprise intermolecular base pairs (pink).