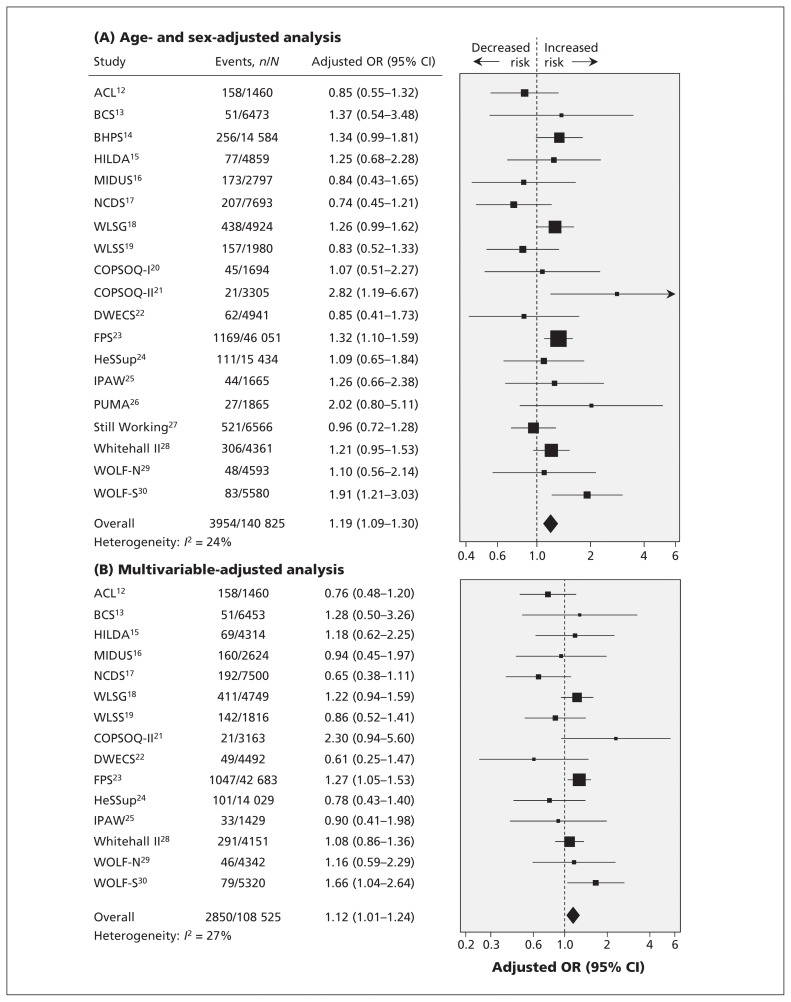
Figure 1:
Study-specific analyses of association between job insecurity and incident diabetes (A) after adjustment for age and sex and (B) after adjustment for age, sex, socioeconomic status, obesity, physical activity, alcohol use and smoking. Values greater than 1.0 indicate an increased risk of incident diabetes. CI = confidence interval, OR = odds ratio. See Table 1 for full study names.