Figure 1. JAK2V617F-mutant ECs have increased cell proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro compared to JAK2WT ECs.
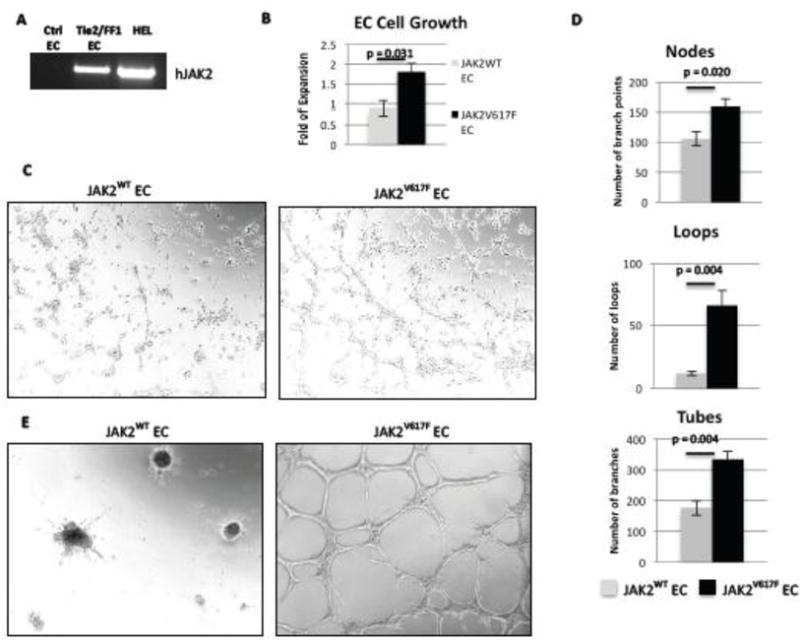
(A) As determined by RT-PCR, human JAK2V617F was expressed in ECs from Tie2/FF1 mice, but not in ECs from control mice. Human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells were used as the positive control. (B) JAK2V617F ECs proliferated more than JAK2WT EC (2.0-fold, p = 0.031). Results of 2 independent experiments (with triplicate in each experiments) are shown here. (C) JAK2WT and JAK2V617F ECs (6×104) were seeded in Matrigel matrix. EC tube formation was observed after an 8-hour incubation. A representative picture is shown. Magnification: 100×. (D) Quantification of tube formation was performed on images taken at 40× magnification by counting the number of nodes (or branch points), loops, and tubes in 4 non-overlapping fields. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=4). Data are from one of two independent experiments that gave similar results. (E) The tubular structures formed by the JAK2V617F ECs in vitro were more stable than the JAK2WT ECs after 24-hour incubation.
