Figure 2. Cytokine-Induced Memory-Like NK Cells Respond to Primary AML Cells Expressing Inhibitory MHC Class I Ligands.
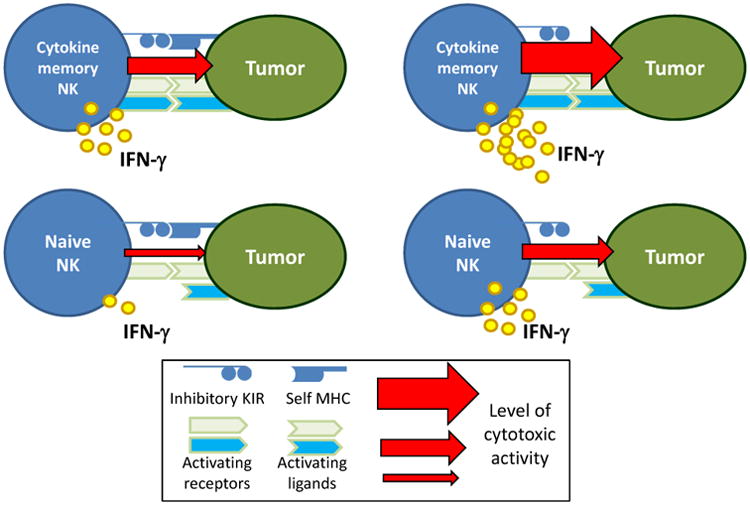
(Left) Engagement of inhibitory killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) expressed by conventional, naïve NK cells normally limits their activation. However, cytokine-induced memory-like NK cells expressing inhibitory KIR recognizing MHC class I expressed by primary AML blasts exhibited enhanced IFN-γ production, compared to control or naïve NK cells. The precise activating signal in this context is currently unknown, although cytokine-induced memory-like NK cells have increased expression of a number of activating receptors. In addition to IFN-γ production, human memory-like NK cell exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity against leukemia targets, compared to control NK cells from the same donors. (Right) In the setting of KIR to KIR-ligand mismatch, memory-like NK cells also have superior responses to conventional or naïve control cells.
