Fig. 1.
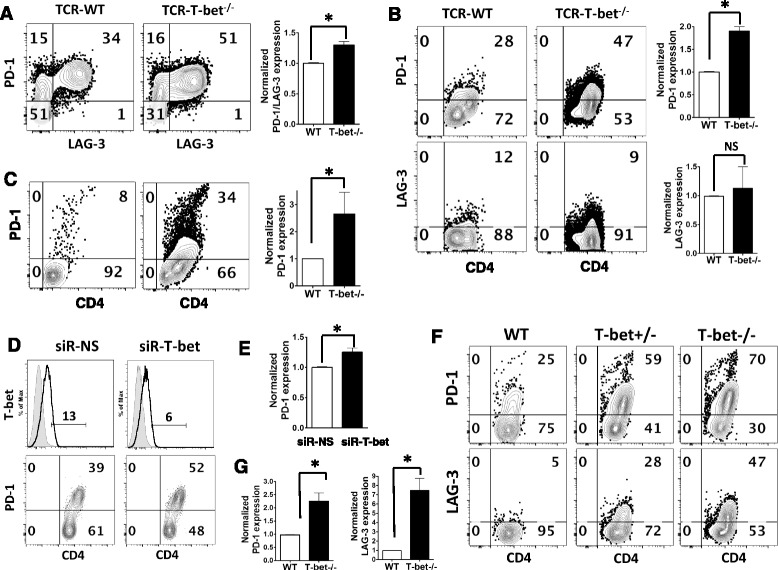
T-bet suppresses the expression of inhibitory receptors in myelin-specific CD4 T cells. a Splenocytes from naive TCR-WT and TCR-T-bet −/− mice were activated with MBP Ac1-11 for 72 h. b The activated cells were then rested for 4 days and c reactivated with MBP Ac1-11 for 2 days. The expression of PD-1 and LAG-3 was determined by flow cytometry. One to two mice from each group were analyzed in each independent experiment, and flow data are representative of three independent experiments. The percentage of PD-1 and/or LAG-3 expressing cells in T-bet−/− group was normalized to that in WT group, and group means were calculated and compared. d–e Splenocytes from naïve TCR-WT mice were transfected with siR-NS or siR-T-bet for 18 h, then activated with MBP Ac1-11 for 3 days. PD-1 expression was determined by flow cytometry while T-bet expression was determined by intracellular staining. Flow data are representative of three independent experiments. The percentage of PD-1 expressing cells in siR-T-bet treated cells was normalized to that in siR-NS treated cells, e and group means were calculated and compared. f–g Naïve WT/B6, T-bet+/−/B6, and T-bet −/−/B6 mice were immunized with MOG 35-55. The draining lymph node cells were isolated on day 8 after immunization and stimulated with MOG 35-55 for 3 days. The expression of PD-1 and LAG-3 was determined by flow cytometry. One to three mice from each group were analyzed in each independent experiment and flow data are representative of three independent experiments. The percentage of PD-1 or LAG-3 expressing cells in T-bet−/− group was normalized to those in WT group, and group means were calculated and compared. Cells were gated on CD4+ CD44+ cells. All error bars denote s.e.m. *P < 0.05
