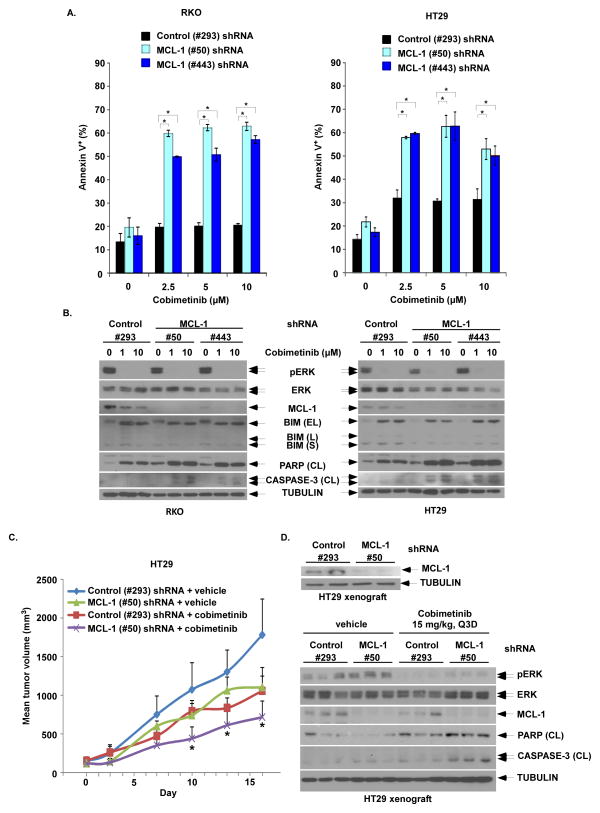
Figure 4. MCL-1 knockdown by shRNA enhances cobimetinib-induced apoptosis and anti-tumor efficacy in BRAF mutant CRC cells and tumor xenografts.
A, RKO and HT29 cells were transduced with lentiviral MCL-1 (#50 or #443) vs control shRNA (#293). Cells with stable expression were then incubated with cobimetinib for 48h at the indicated doses. Apoptosis was analyzed by annexin V+ staining that was quantified using flow cytometry. Mean values were derived from triplicate experiments and bars represent S.D. *p<0.05. B, Apoptosis was also analyzed by expression of cleavage (CL) of PARP and CASPASE-3 by immunoblotting in both cell lines. C, HT29 cells containing stable expression of control (#293) or MCL-1 (#50) shRNA were grown as tumor xenografts in SCID mice. Xenograft-bearing mice with dosed with either vehicle or cobimetinib (15 mg/kg every 3 days by oral gavage) for 14 consecutive days. Xenograft mean tumor volumes are plotted against days of treatment for vehicle- and cobimetinib-treated mice. Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance(*, P < 0.05) is shown for comparison of MCL-1 (#50) shRNA + cobimetinib vs control (#293) shRNA + cobimetinib. D, Pre-treatment expression of MCL-1 in tumors from xenograft-bearing mice was evaluated by immunoblotting (upper panel). Post-treatment expression of pERK/ERK, MCL-1, cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 in tumor xenografts from the 4 groups of tumor-bearing mice were evaluated by immunoblotting (lower panel).