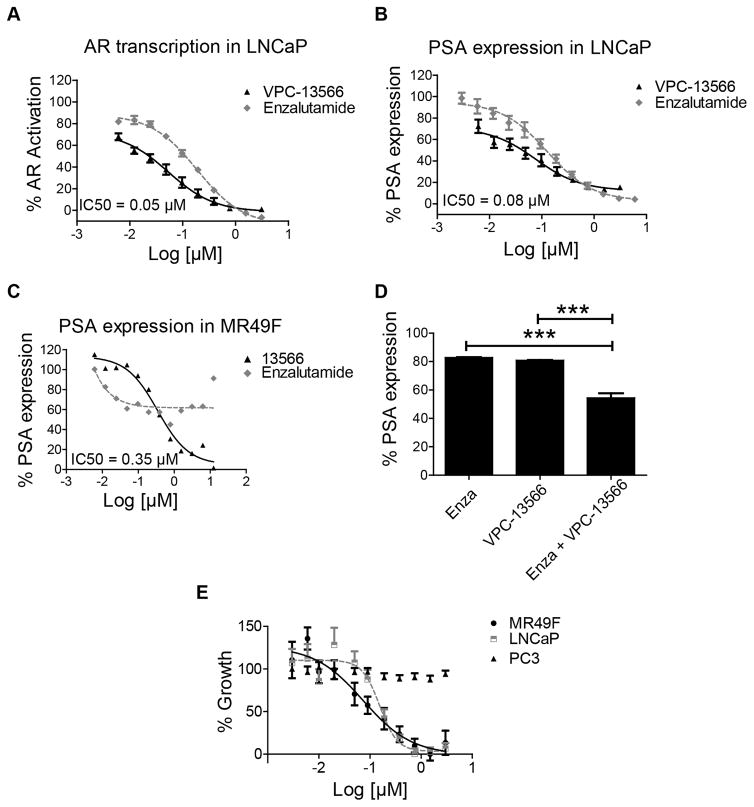
Figure 1. Effect of VPC-13566 on AR transcriptional activity and cell growth.
A- Dose-response inhibition of AR transcriptional activity by VPC-13566 and enzalutamide in LNCaP cells. Data points represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. B–C Effect of VPC-13566 in comparison to enzalutamide on PSA expression in LNCaP cells (B) and enzalutamide resistant cells (MR49F) (C). D- The combination of VPC-13566 (IC25 = 50 nM) and enzalutamide (IC25 = 40 nM) decreases the AR regulated PSA expression in LNCaP cells. E- The effect of VPC-13566 on cell viability in LNCaP, enzalutamide resistant cell line (MR49F) and PC3 cells. % cell viability is plotted in dose dependent manner. Data points represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.