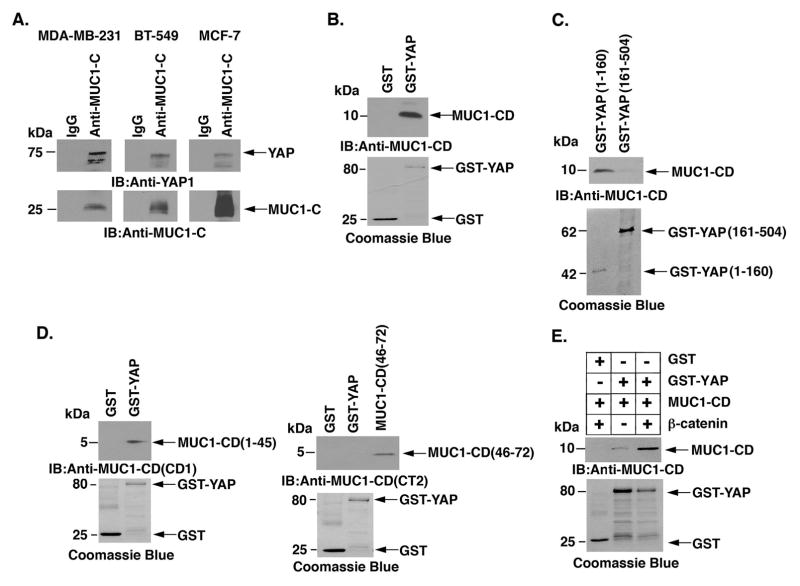
Figure 5. Binding of MUC1-C and YAP.
A, Lysates from MDA-MB- 231 (left), BT-549 (middle) and MCF-7/MUC1-C (right) cells were precipitated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. B, GST and GST-YAP were incubated with purified MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD). The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-C. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. C, GST-YAP(1–160) and GST-YAP(161–504) were incubated with purified MUC1-CD. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-C. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. D, GST and GST-YAP were incubated with MUC1-CD(1–45) (left) or MUC1-CD(46–72) (right). The adsorbates and purified MUC1-CD proteins were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-CD (CD1, left; CT2, right) antibodies. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. E, GST and GST-YAP were incubated with purified MUC1-CD and/or with purified β-catenin. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-CD. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining.