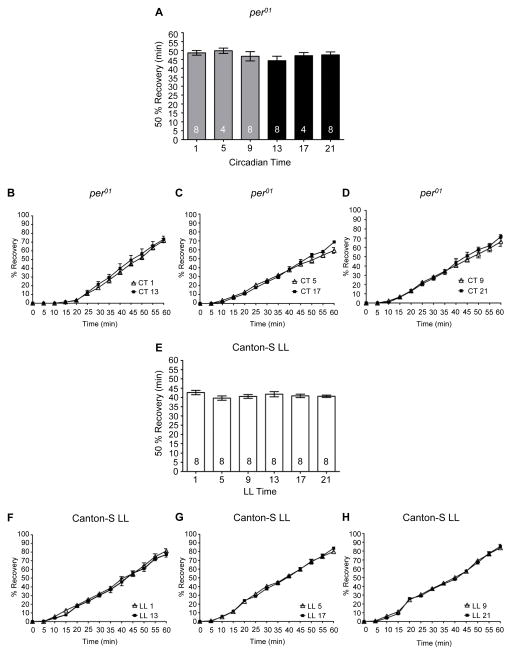
Figure 4. A functional circadian clock is necessary for rhythms in alcohol-induced recovery.
(A) There was no significant time of day difference in the time necessary for 50% of per01 flies to recover from alcohol-induced sedation as assessed by recovery of the righting reflex (ANOVA: F5, 34 = 0.76, p = 0.59). Complete time courses shown for recovery of the righting reflex following alcohol-induced sedation in per01 flies for (B) CT 1 and 13, (C) CT 5 and 17 and (D) CT 9 and 21. (E) There was no significant time of day difference in the time necessary for 50% of CS flies housed under LL conditions to recover from alcohol-induced sedation as assessed by recovery of the righting reflex (ANOVA: F5, 42 = 0.95, p = 0.46). Complete time courses shown for recovery of the righting reflex following alcohol-induced sedation in CS flies in LL for (F) 1 and 13, (G) 5 and 17 and (H) 9 and 21.