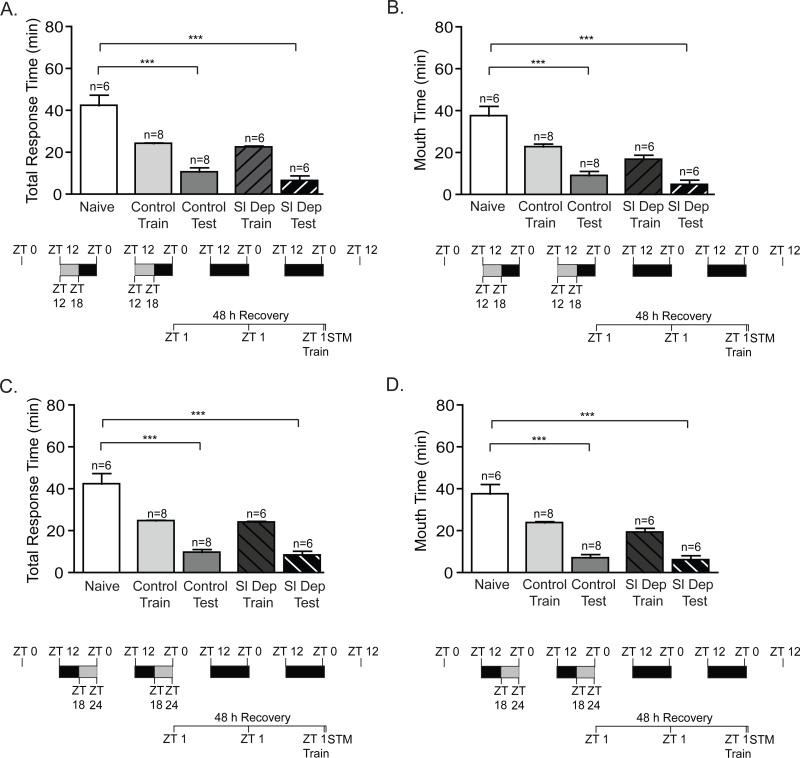
Figure 5. Impairment in STM induced by 2 consecutive nights of chronic sleep deprivation is alleviated after 48 hours.
A and B) Animals sleep deprived (Sl Dep Test) during the first 6 hours of the night for two nights and allowed to recover for 55 hours prior to training exhibited STM with significantly shorter total response time compared to naïves and similar to trained non-sleep deprived animals (Control Test): A) Total response time (one-way ANOVA F(4,29) = 32.20, P < 0.0001). Asterisks represent Bonferroni's post-hoc analyses ***P < 0.001. B) Time the seaweed was retained in the mouth (one-way ANOVA F(4,29) = 25.30, P < 0.0001). Asterisks denote significant differences with ***P < 0.001. C and D) Animals sleep deprived for two nights during the last 6 hours of the night and trained approximately 49 hours after sleep deprivation at ZT 1 demonstrated robust STM: A) Total response time (one-way ANOVA F(4,29) = 36.92, P < 0.0001). Asterisks represent Bonferroni's post-hoc analyses ***P < 0.001. D) Time the seaweed was retained in the mouth (one-way ANOVA F(4,29) = 32.32, P < 0.0001). Asterisks denote significant differences with ***P < 0.001.