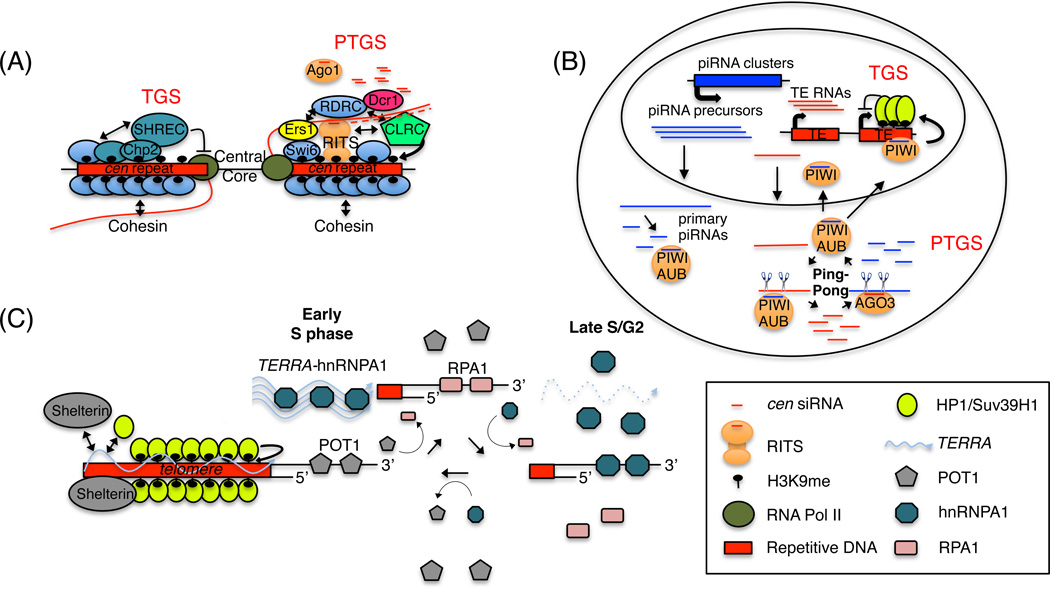
Figure 2.
ncRNA-mediated silencing and telomere regulation. (A) siRNA-dependent H3K9 methylation at the fission yeast pericentromeric regions. A network of interactions among RNAi complexes (RITS, RDRC, Dcr1), cen lncRNAs (red wavy line), and CLRC (green pentagon) creates siRNA and H3K9me amplification loops at centromeres. This leads nucleation and spreading of H3K9me and the recruitment of the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) proteins, Swi6 (blue oval) and Chp2 (turquoise). Chp2 in complex with SHREC represses RNA Pol II (green circle) transcription (TGS), and Swi6 facilitates RNAi-dependent PTGS via its Ers1-dependent interactions with RDRC. Swi6 also interacts cohesin and is required for its recruitment to cen repeats. In the absence of CLRC, RNAi complexes or Swi6, cohesin recruitment is lost and cells display chromosome segregation defects. (B) piRNA silencing in D. melanogaster maternal germ cells. piRNA clusters and transposons are shown in blue and red, respectively. Cytoplasmic degradation of TE transcripts by the Piwi family proteins (Aubergine (Aub), Piwi and Argonaute-3 (Ago3) is depicted. Iterative cycles of Piwi/Aub and Argonaute-3 (Ago3) cleavage events in the cytoplasm amplify the piRNA signal and degrade TE transcripts. Also, piRNA-Piwi complexes can be imported into the nucleus where they mediate TGS silencing via the recruitment of HP1/Su(var)3–9 proteins (yellow oval). (C) TERRA and telomere regulation. TERRA (blue wavy line) is a structural component of telomeres upon which Sheltrin (gray oval), HP1/Suv39H1 (lime green circle), and other silencing complexes assemble. TERRA also facilitates the RPA (pink rectangle)-to-POT1 (gray pentagon) transition via binding to hnRNAP1 (teal octagon). See text for details.