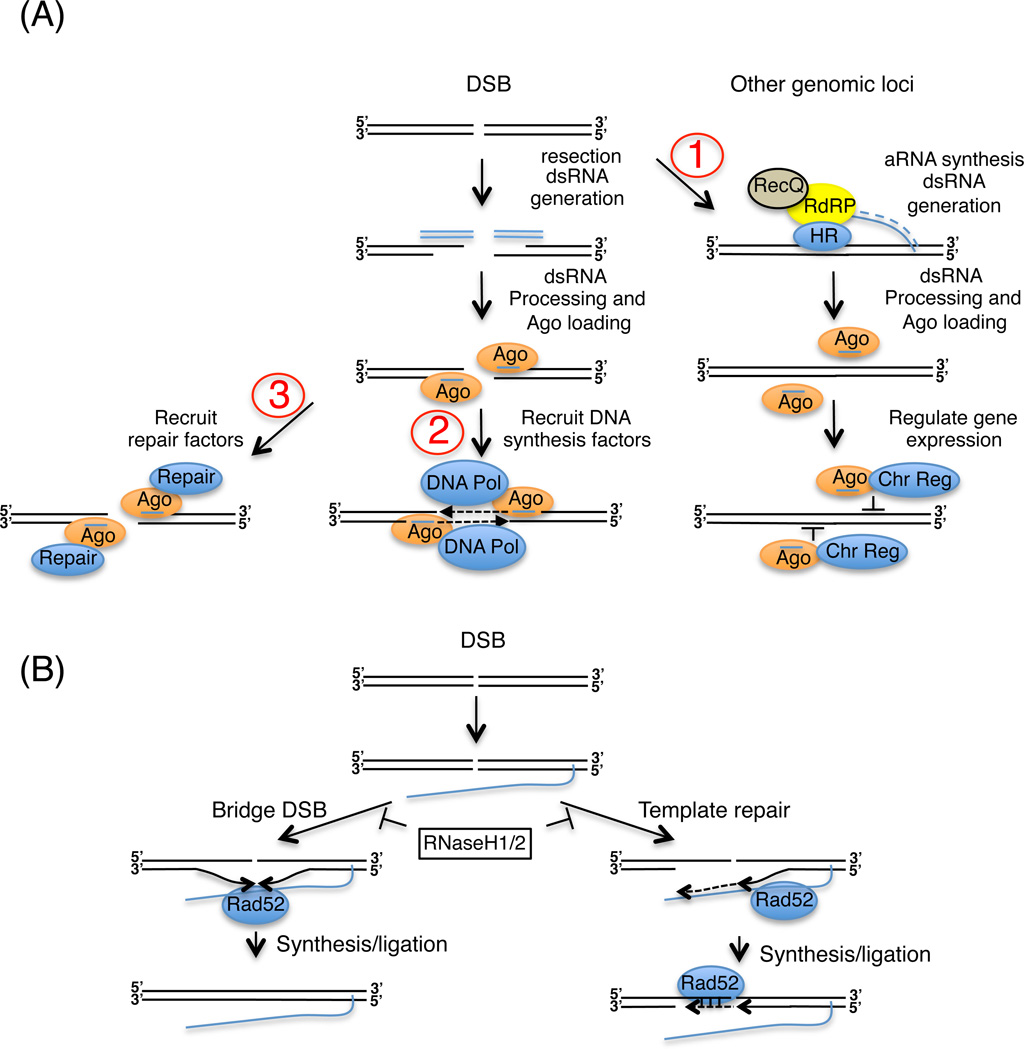
Figure 4.
ncRNAs regulation of DSB repair. (A) diRNA-mediated DSB repair. DSBs induce RNAi-dependent diRNA production, which once loaded onto Ago (orange oval) target Ago recruitment to DSBs (pathways 2 and 3) or other sites around the genome (pathway 1). In 1, diRNAs recruit Ago to sites (other than the DSB) around the genome (for example rDNA in N. crassa), potentially regulating their transcription in a manner that favors DSB repair. In 2, diRNAs recruit Ago and DNA polymerases (blue oval) to the DSB to catalyze a synthesis-dependent repair process. In 3, diRNA-programmed Ago complexes recruit repair proteins to the DSB. (B) lncRNA-mediated DSB repair. RNA molecules (blue line) complementary to the DSB may serve as a bridge (left) or template (right) for repairing DSBs. RNase H1/H,2 inhibit this repair mechanism by removing RNA:DNA hybrids. On the other hand, Rad52 (blue oval), which promotes RNA:DNA hybrid formation in vitro, is proposed to stimulate DSB repair by annealing the RNA to the DSB. RNA:DNA hybrids are thought to promote the precise re-ligation of a DSB (left) or reverse transcriptase-dependent synthesis and re-ligation (right) at the DSB. These depicted mechanisms may operate in non-dividing mammalian cells (Wei et al., 2015).