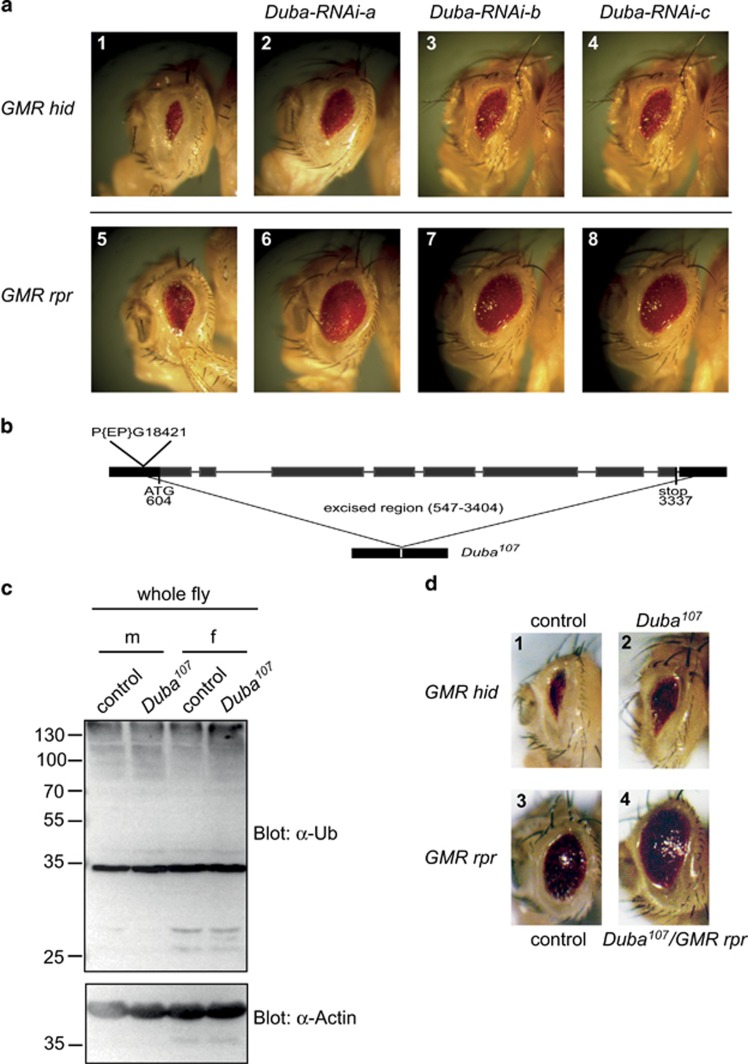
Figure 1.
Loss of DUBA suppresses Rpr- and Hid-induced cell death in the eye and leads to accumulation of poly-ubiquitylated proteins. (a) GMR-hid- or GMR-rpr-expressing flies were crossed with Duba-RNAi fly lines. Genotypes: (1) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/+ ey-Gal4/TM3; (2) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/+ ey-Gal4/Duba-RNAi-a; (3) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/Duba-RNAi-b; ey-Gal4/+ (4) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/Duba-RNAi-c; ey-Gal4/+ (5) ey-Gal4/+ GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/TM3; (6) ey-Gal4/+ GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/Duba-RNAi-a; (7) Duba-RNAi-b/+ GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/+ (8) Duba-RNAi-c/+ GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/+. (b) Generation of a Duba-null allele (Duba107). Shown is the longest transcript (CG6091-RE). The complete coding region was removed by imprecise P-element excision of P{EP}CG6091[G18421]. (c) Loss of Duba leads to increased levels of poly-ubiquitylated proteins. Male (m) or female (f) Duba107 or control flies (precise excision) were lysed in SDS-loading buffer and analysed by western blotting. (d) GMR-hid- or GMR-rpr-expressing flies were crossed with Duba107 flies. Genotypes: (1) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/cyo; ey-Gal4/TM6b; (2) GMR-hid, GMR-Gal4/+ Duba107; (3) GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/TM6b; (4) GMR-rpr, GMR-Gal4/Duba107