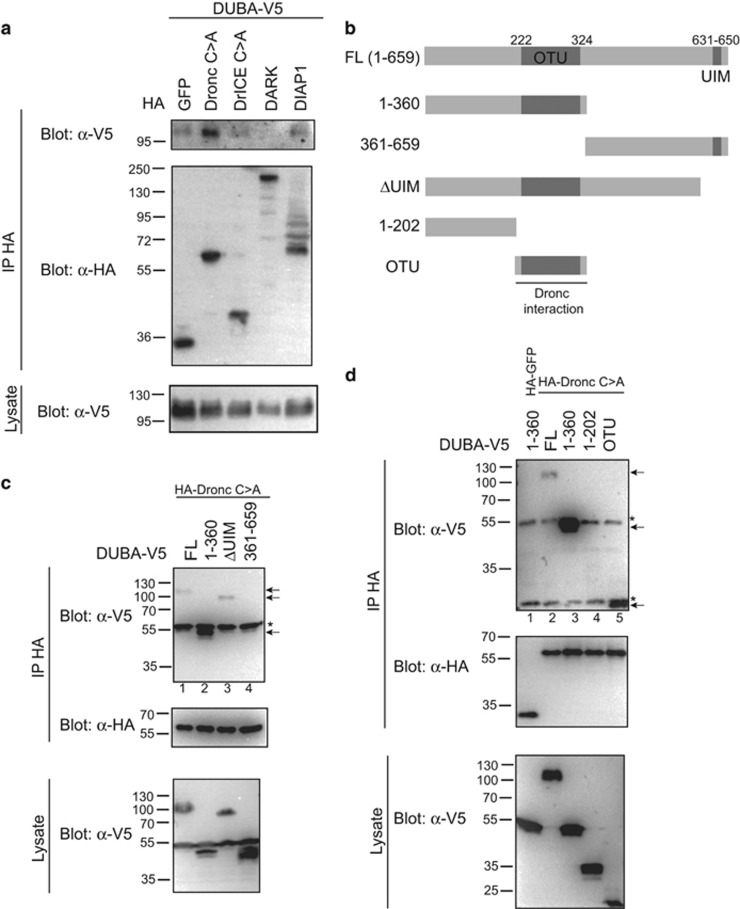
Figure 2.
DUBA interacts with DIAP1 and the initiator caspase Dronc. (a) S2 cells were transfected with expression vectors for DUBA (V5-tagged) and HA-GFP, HA-Dronc C>A (caspase-inactive), HA-DrICE C>A (caspase-inactive), HA-DARK or HA-DIAP1 as indicated, and lysed for anti-HA IP. IP eluates and lysates were analysed by immunoblotting with α-HA or α-V5 antibodies. Co-IP of DUBA was detected with HA-Dronc and HA-DIAP1 (weak). (b) Schematic overview of DUBA domain structure (OTU, ovarian tumour domain; UIM, ubiquitin-interacting motif) and deletion constructs used in c). (c and d) Co-IP to determine the interaction domain of DUBA with Dronc. The experiment was performed as in a, with the indicated V5-tagged fragments of DUBA. Positive Co-IP of DUBA fragments is indicated by arrows. Interaction is mediated through the N-terminal half of DUBA (c, lane 2) and within this part by the OTU domain (d, lane 5). Cross-reacting IgG bands are marked with *