Figure 1.
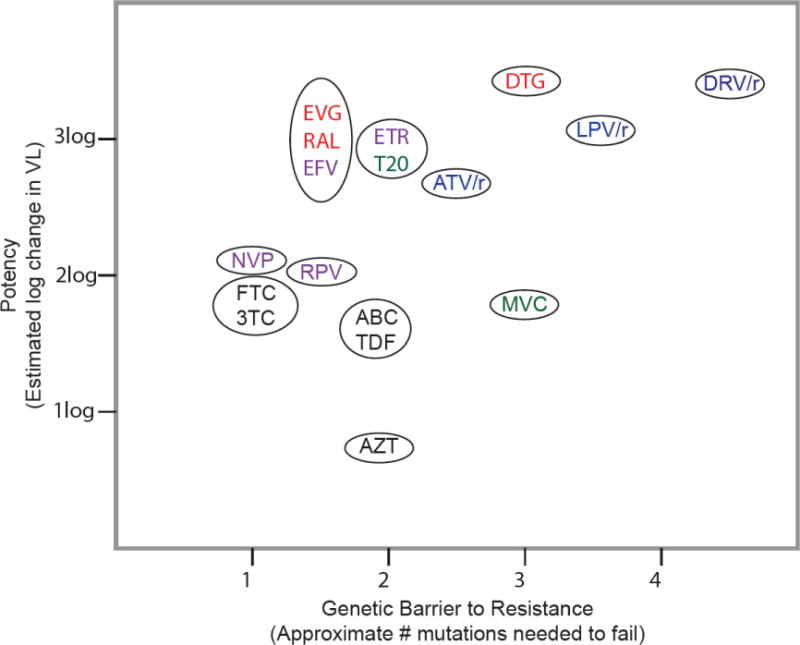
ARV potency versus genetic barrier to resistance.
Abbreviations: ARV: antiretroviral; VL: viral load; ABC: abacavir; ATV/r: boosted atazanavir; DRV/r: boosted darunavir; DTG: dolutegravir; EFV: efavirenz; FTC: emtricitabine; EVG: elvitegravir; T20: enfuvirtide; ETR: etravirine; 3TC: lamivudine; LPV/r: boosted lopinavir; MVC: maraviroc; NVP: nevirapine; RAL: raltegravir; RPV: rilpivirine; and TDF: tenofovir. ARVs in black font are nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), those in purple font are non-NRTIs (NNRTIs), those in blue font are protease inhibitors (PIs), those in red font are integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), and those in green font are entry inhibitors. ARVs appearing together in the same ellipse should be considered to have roughly equivalent potencies and genetic barriers to resistance.
