Figure 3.
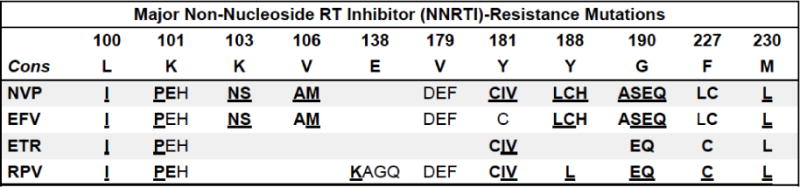
Summary of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drug resistance mutations.
Bold/underline: High-level reduced susceptibility or virological response. Bold: reduced suceptibility or virological response. Plain text: reduced susceptibility in combination with other NNRTI-resistance mutations. Asterisk: increased susceptibility. Abbreviations: nevirapine (NVP), efavirenz (EFV), etravirine (ETR), rilpivirine (RPV). Synergistic combinations: V179D+K103R reduce NVP and EFV susceptibility >10-fold. Y181C+V179F cause high-level ETR and RPV resistance. ETR genotypic susceptibility score (GSS): Y181IV (3.0); L100I, K101P, Y181C, M230L (2.5); V90I, E138A, V179F, G190S (1.5); A98G, K101EH, V106I, V179DT, G190A (1.0); 3.0 high-level. V90I, A98G, V106I, E138A, V179DT, G190A/S have little effect on ETR susceptibility unless they occur with a bolded mutations. Additional accessory mutations: V90I (ETR), A98G (NVP, EFV, ETR, RPV), V108I, V179T (ETR), V179L (RPV), P225H (EFV), K238T (NVP, EFV), L318F (NVP). References: http://hivdb.stanford.edu/DR/NNRTIResiNote.html.
