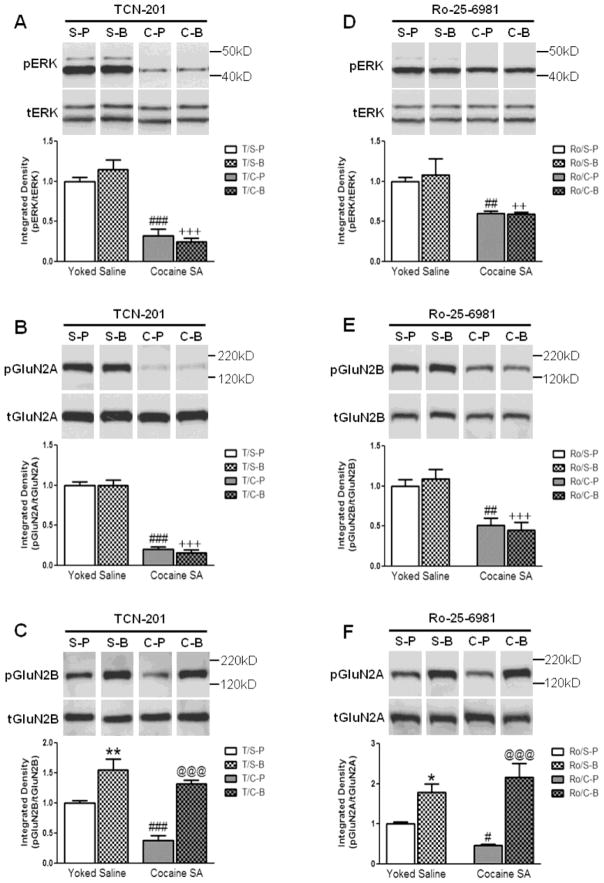
Figure 4.
The effect of intra-prelimbic TCN-201 or Ro-25-6981 infusion before PBS or BDNF on (A, D) pERK, (B, F) pGluN2A, and (C, E) pGluN2B levels in the prelimbic cortex of rats with a cocaine SA or yoked-saline history 2 hr after infusion. (A–C) TCN-201 had no effect on the ability of cocaine to decrease levels of (A) pERK or (B) pGluN2A in the prelimbic cortex; (S-P vs. C-P; ###p<0.001). However, TCN-201 prevented the ability of BDNF to reverse the cocaine-induced decrease in pERK and pGluN2A levels (S-B vs. C-B, +++p<0.001). (C) TCN-201 did not prevent the ability of cocaine to decrease pGluN2B levels (S-P vs. C-P, ###p<0.001). However, in the presence of TCN-201, BDNF was able to increase pGluN2B levels in the prelimbic cortex of rats with a cocaine SA or yoked-saline history (C-P vs. C-B, @@@p<0.001 and S-P vs. S-B, **p<0.01, respectively). (D–F) Ro-25-6981 had no effect on the ability of cocaine to decrease (D) pERK and (E) pGluN2B levels in the prelimbic cortex (S-P vs. C-P; ##p<0.01). However, Ro-25-6981 prevented the ability of BDNF to reverse the cocaine-induced decrease in pERK and pGluN2B levels (S-B vs. C-B, ++p<0.01 and +++p<0.001, respectively). (F) Ro-25-6981 did not prevent the ability of cocaine to decrease pGluN2A (Y1375) levels (S-P vs. C-P, #p<0.05). However, in the presence of Ro-25-6981, BDNF was able to increase pGluN2A levels in the prelimbic cortex of rats with a cocaine SA or yoked-saline history (C-P vs. C-B, @@@p<0.001 and S-P vs. S-B, *p<0.05, respectively). Representative immunoblot images above bar graphs were prepared using images taken from different parts of the same gel. The positions and sizes of the protein molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the right. The bar graphs indicate the mean ± SEM. S=Yoked-Sal, C=Cocaine SA, P=PBS, B=BDNF, T=TCN-201, Ro=Ro-25-6981. N=6–8 per group.