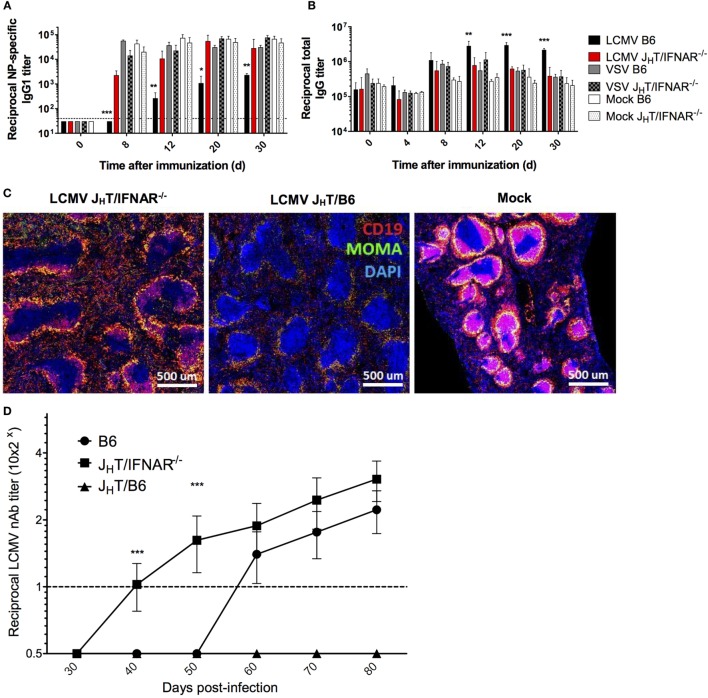
Figure 7.
B cell-specific disruption of IFNAR restores NP-specific Ab responses and accelerates the development of LCMV nAbs. (A–C) B6, JHT/IFNAR−/−, or JHT/B6 mice (four per group) were infected with LCMV Cl13 (black for B6; red for JHT/IFNAR−/−), VSV (gray), or were mock infected (white). Plain bars represent B6 mice and checkered bars JHT/IFNAR−/− B cell bone marrow chimeric mice. (A) NP-specific IgG1 and (B) total IgG responses monitored using ELISA on d8 following infection/NP53-CGG immunization. (C) Splenic follicular structures visualized using immunofluorescent staining of CD19 (red), MOMA-1 (green), and DAPI (blue) on spleen sections obtained on d8 postinfection. (D) Neutralization assay showing accelerated nAb responses in JHT/IFNAR−/− chimeric mice upon infection with LCMV Cl13. (A–C) Representative of two independent experiments. (D) Compilation of three independent experiments (B6 mice, n = 21; JHT/IFNAR−/− mice, n = 25; JHT/B6 mice, n = 8). Statistical analysis was performed by individual T-tests between experimental groups and the mock-infected group for (A–C) and one-way ANOVA for (D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. The dotted line represents detection threshold.