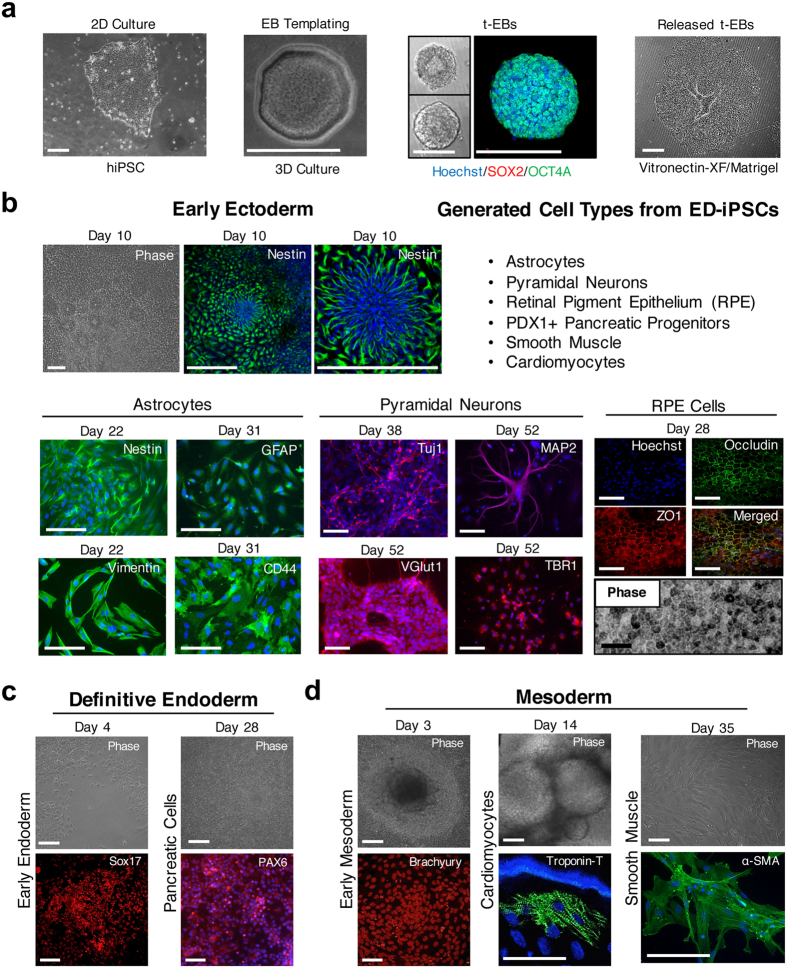
Figure 1. Overview of differentiation strategies applied to ED-iPSC lines.
Multi-lineage differentiation to ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm specialized cell types. (a) ED-iPSC lines were maintained as 2D feeder-free cultures, then differentiated from uniformly sized embryoid bodies (EB) formed in custom lithography patterned well arrays (200 μm t-EBs). The t-EBs were plated onto Matrigel or Vitronectin-XF for differentiation. Scale bars are 200 μm. (b) Early Ectoderm cell types. Differentiation of plated t-EBs to astrocytes, neurons, and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells was done from neural stem cell (NSC) precursors. Neural rosettes appeared by day 7 upon addition of STEMdiff Neural Induction Medium. Early differentiating neural populations expressed intermediate filament markers Nestin (green; shown ED-iPSC F3.6.1) and Vimentin (green; shown ED-iPSC F3.5.2). Functional astrocytes expressed GFAP (green; shown ED-iPSC H3.3.1) and CD44 (green; shown ED-iPSC A2.2.2) by day 31 of differentiation. Differentiated neurons expressed β-III-tubulin (Tuj1; red; shown is ED-iPSC A2.2.2), MAP2 (red; shown is H9 hESC), VGlut1 (red; shown is ED-iPSC F3.5.2) and TBR1 (red; shown ED-iPSC F3.5.2). Representative differentiation to RPE cells (shown ED-iPSC F3.5.2), stained for Occludin (green) and ZO1 (red) tight junction markers showing cobblestone morphology. Scale bars are 50 μm. (c) Definitive endoderm, representative differentiation to pancreatic progenitor cells (shown ED-iPSC A2.2.2). Scale bars are 50 μm. (d) Mesoderm cell types. Representative differentiation to cardiomyocytes (shown is ED-iPSC A2.2.2) and smooth muscle cells (shown ED-iPSC F3.5.2). The hESC line WA09 (H9) when compared followed similar protocols. Scale bars are 50 μm.