Figure 6.
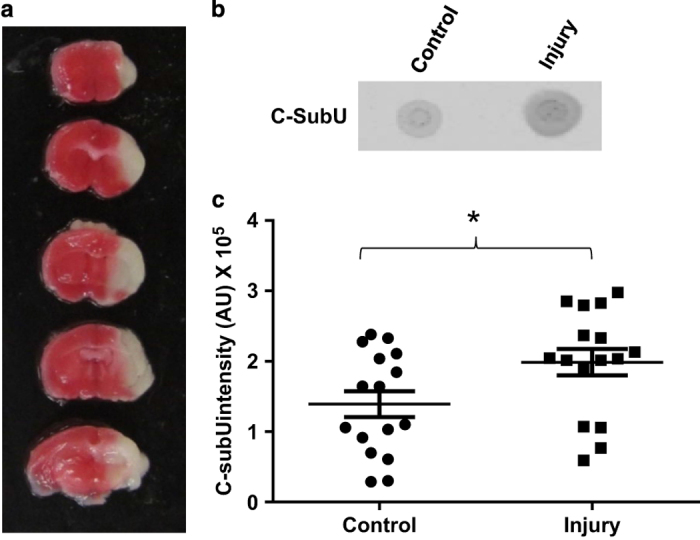
HI brain injury is associated with increased C-subunit levels in the channel-forming fraction. (a) Image of a whole brain stained with TTC (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride) from a representative mouse subjected to HI brain injury. Viable tissue is stained red while the infarct is unstained or white. (b) Dot blot for C-subunit prepared using C-subunit antibodies. The extracts from the injured side of the brain showed higher amounts of C-subunit compared with the non-injured side. (c) Densitometry analysis of the C-subunit dot blots of chloroform extracts from brain uninjured (control) and damaged (injury) hemispheres showing increased C-subunit levels in the damaged hemisphere (*P<0.05, Mann–Whitney nonparametric test, n=16 animals).
