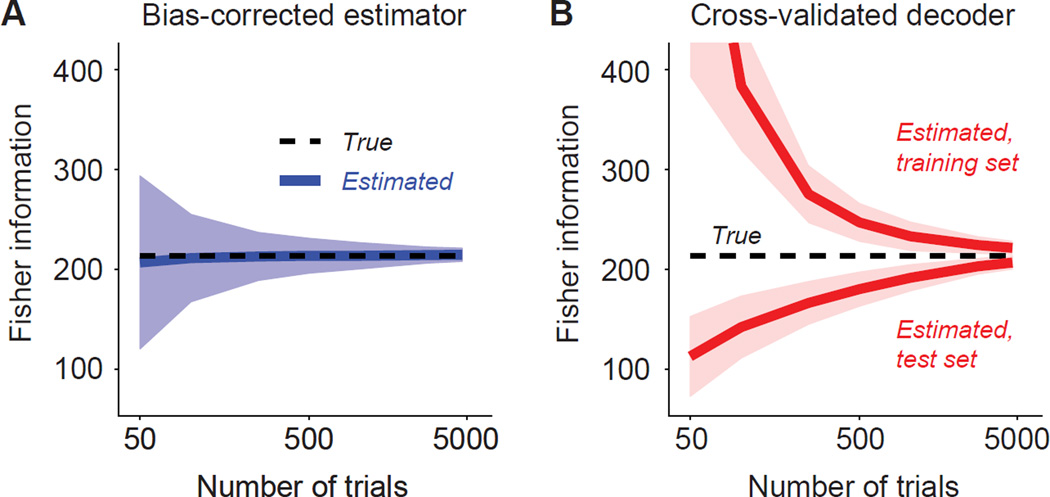
Figure 2. Estimating Fisher information from population recordings.
Two estimators of Fisher information are shown that accurately capture the information present in a neuronal population. Simulations are based on 50 neurons and 200 experiments, where each experiment involves a different set of parameters for the filters representing each neuron. (a) The direct estimator with analytical bias correction (blue line) provides an unbiased estimate of the true information (dotted line). Shaded areas represent ±1 standard deviation of the estimate. (b) The performance of a trained decoder on left-out data (test set) provides a lower bound on the true information and approaches the true information when there are a sufficient number of trials. Both panels from Kanitscheider et al. 2015a.