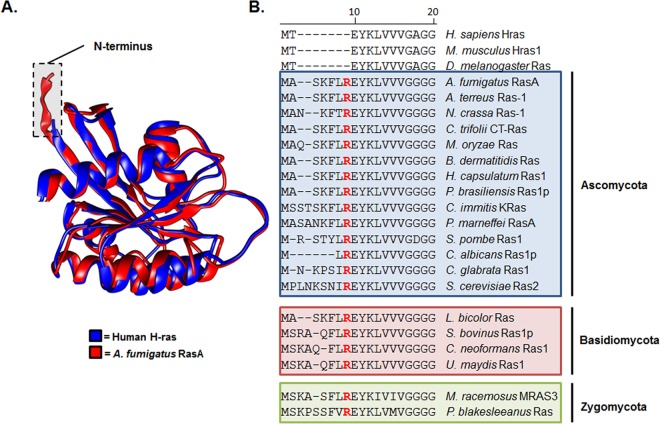
FIG 1 .
The RasA protein displays an extended N terminus harboring an invariant arginine residue. (A) Comparison of Ras protein structure. A ribbon representation of H-ras (blue) (16) (PDB entry 4EFL) was superimposed with the predicted structure of RasA (red) using UCSF Chimera (54). Chimera was developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco. Homology modeling of RasA structure was predicted using the known H-Ras structure as a template. The RasA amino acid sequence was mapped to the H-Ras structure using ProtSkin (55). The figure displays RasA amino acids 1 to 166. (B) Multiprotein alignment of N-terminal RasA homolog sequences from multiple fungal species and higher eukaryotes. Organisms and Ras homologs (with GenBank accession numbers in parentheses) employed for alignment include Homo sapiens H-ras (AAM12630.1), Mus musculus Hras1 (AAQ81319.1), Drosophila melanogaster Ras1 (AAF15514.1), Aspergillus fumigatus RasA (EAL91488.1), Aspergillus terreus Ras-1 (EAU31971.1), Neurospora crassa Ras-1 (P22126.1), Colletotrichum trifolii CT-Ras (AAC03781.1), Magnaporthe oryzae Ras (ELQ42826.1), Blastomyces dermatitidis Ras (EEQ88958.1), Histoplasma capsulatum Ras (EEH06649.1), Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Ras1p (AAZ81605.2), Coccidioides immitis K-Ras (KMU89545.1), Penicillium marneffei RasA (EEA28487.1), Schizosaccharomyces pombe Ras1 (CAB11218), Candida albicans Ras1p (AF177670.1), Candida glabrata Ras (XP_445167.1), Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ras2 (DAA10447.1), Laccaria bicolor Ras (AAD01987.1), Suillus bovinus Ras1p (AF250024.1), Cryptococcus neoformans Ras1 (AF294647.1), Ustilago maydis Ras1 (AAO19640.1), Mucor racemosus MRAS3 (AAA83379.1), and Phycomyces blakesleeanus Ras (OAD74690.1). The areas shaded in blue, red, and green denote organisms characterized as Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes, or Zygomycetes, respectively. Note the invariant arginine residue (highlighted as red text) located in the same position for each fungal RasA homolog.