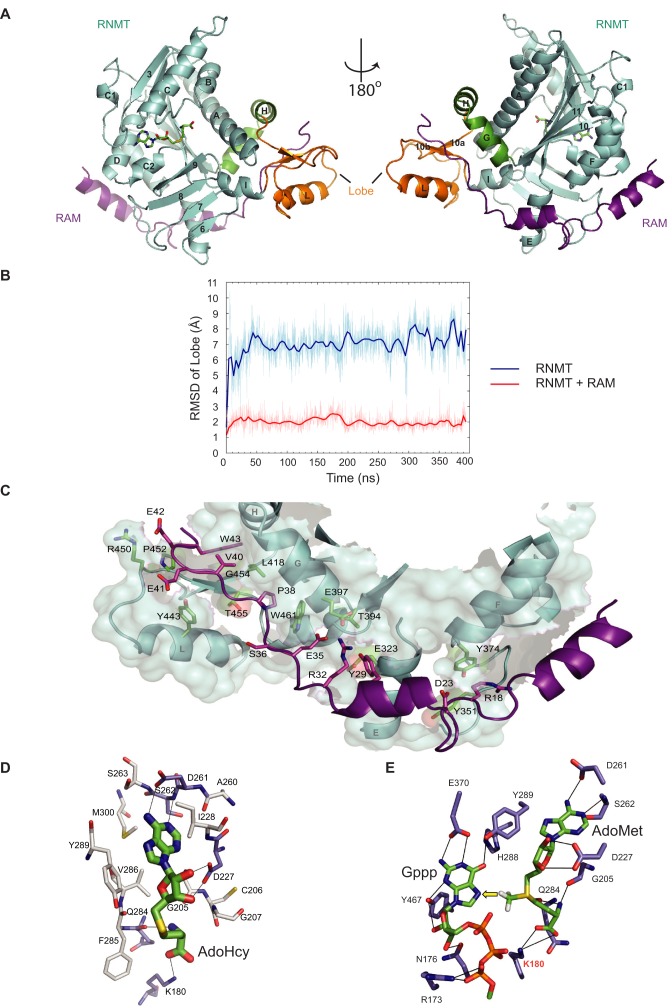
Figure 1.
RNMT-RAM crystal structure. (A) RNMT 165–476 (cyan) and RAM 2–45 (magenta) crystallised with AdoHcy. The RNMT lobe is highlighted in orange and α-helix hinge in green. Secondary structure attribution was performed with DSSP. (B) Time evolution of RMSD of the lobe backbone (residues 419–458) in molecular dynamics simulations, with RAM (red) and without (blue). The RNMT-RAM crystal structure was used as a reference. (C) RNMT and RAM amino acids involved in polar interactions as determined using the PISA server (EMBLI-EBI) are shown as sticks. (D) AdoHcy binding site in RNMT shown with amino acids involved in hydrogen bond formation (purple) and hydrophobic interactions (white). (E) Representative structure from MD simulation of RNMT–RAM with the ligands AdoMet and Gppp. Initial positioning of Gppp was based on previous structure (PDB: 1RI2) (15). For clarity, only residues involved in electrostatic interactions are shown. The yellow arrow depicts in-line transfer of the methyl group. Lines represent hydrogen bonds in panels D and E.