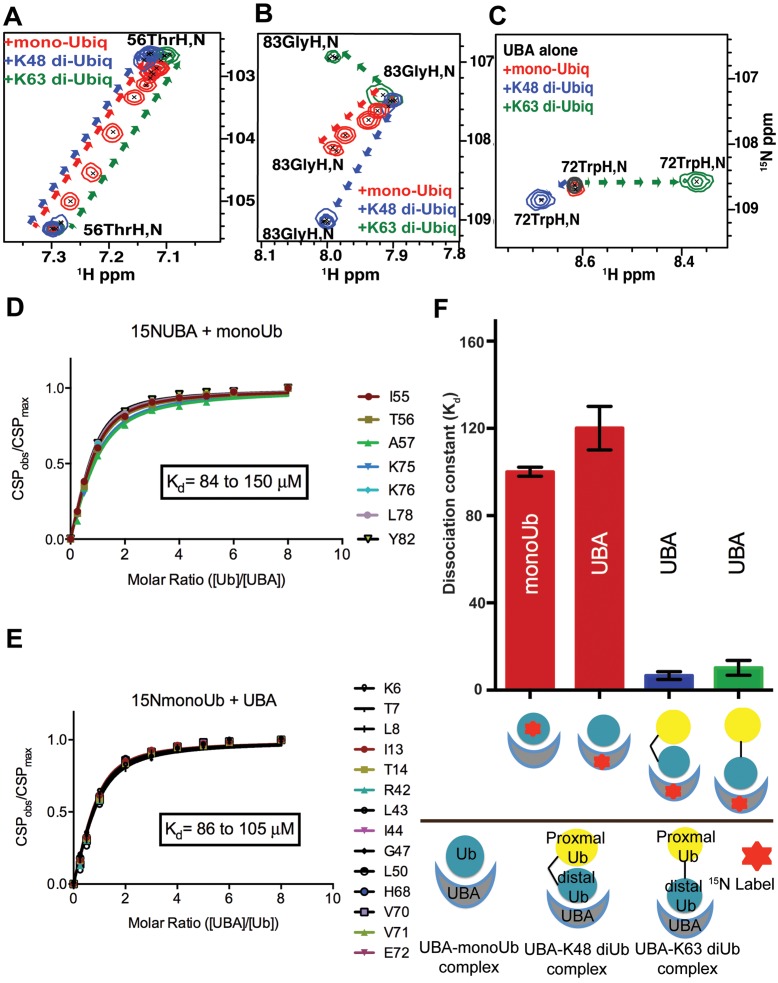
Figure 5.
TDP2 UBA binds Ubs with different modes of binding. (A) Chemical shift titration profiles of TDP2 UBA Thr56 for binding with monoUb and diUbs (K48 or K63-linked) at UBA:Ub ratios of 1:0, 4:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4 and 1:6 show shifting of the peaks in the same direction for all, but in fast exchange for monoUb (red) and slow-intermediate exchange for diUbs (blue and green). (B) Chemical shift titration profiles of TDP2 UBA Gly83 for binding with monoUb and diUbs (K48 or K63-linked) show shifts in different directions. (C) Chemical shift titration profiles of CeTDP2 UBA Trp72 for binding with monoUb and diUbs (K48- or K63-linked) show no shift for monoUb binding, but shifts in different directions for the two diUbs. (D) The combined CSPs of significantly shifted peaks from 15N labeled CeTDP2 UBA at indicated molar ratios with monoUb. The range of Kd values calculated for the chosen residues is shown on the graph. (E) CSPs of significantly shifted peaks from 15N labeled monoUb titrated with increasing concentration of CeTDP2 UBA. The range of Kd values calculated for the chosen residues is shown on the graph. (F) Binding affinity averages from chemical shift titrations of different combinations of CeTDP2 UBA and Ubs are shown, with error bars for standard error of mean. Text labels inside each bar indicate the protein that was 15N labeled in that experiment. Ligand for the corresponding binding experiment is shown as a schematic cartoon label under the X-axis. The bottom half of the panel shows what each schematic cartoon represents. The kinked and straight black bars between two Ub moieties stands for the K48- and K63-linkage, respectively. The cartoons do not depict the actual binding poses (they are not meant to show that UBA only interacts with the distal Ub moieties of diUbs).