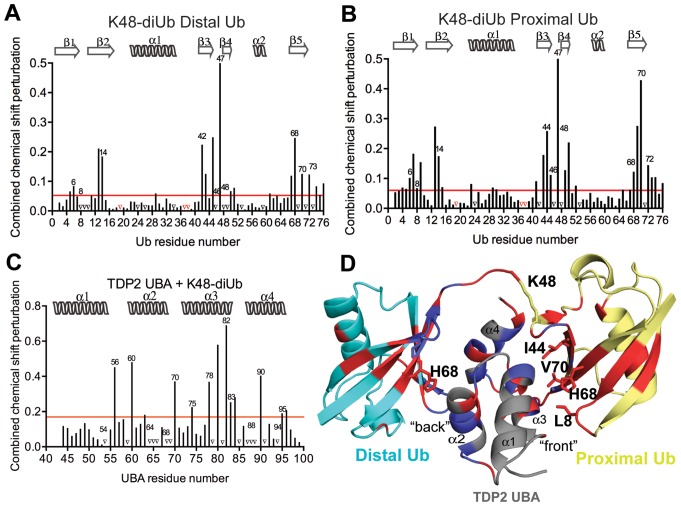
Figure 6.
Interaction of K48-linked diUb with UBA. (A) Per residue chemical shift perturbation map of 15N labeled distal Ub residues when K48-linked diUb was titrated with increasing concentrations of CeTDP2 UBA. The red line denotes cut-off for significance; set at 1 standard deviation (1 σ) from all the weighted averaged chemical shift values. Peaks that vanished during the titration are represented by black triangles on the graph and prolines, which are excluded from this analysis, indicated with red triangles. (B) Per residue chemical shift perturbation map of 15N labeled proximal Ub residues when K48-linked diUb was titrated with increasing concentrations of CeTDP2 UBA. Significance denoted by a red line defined as in A. Prolines and amino acids with signals that disappeared are represented by red and black triangles, respectively. (C) Per residue chemical shift perturbation map of 15N labeled CeTDP2 UBA residues when it was titrated with increasing concentrations of K48-linked diUb. Significance as in A. (D) A hypothetical model of one molecule of TDP2 UBA binding to one molecule of K48-linked diUb. Significantly shifted residues for TDP2 UBA and Ub are colored in red with some of these residues that determine the interaction surface on each Ub moiety labeled. Peaks that disappeared upon titration are colored in blue on both UBA and Ub moieties.