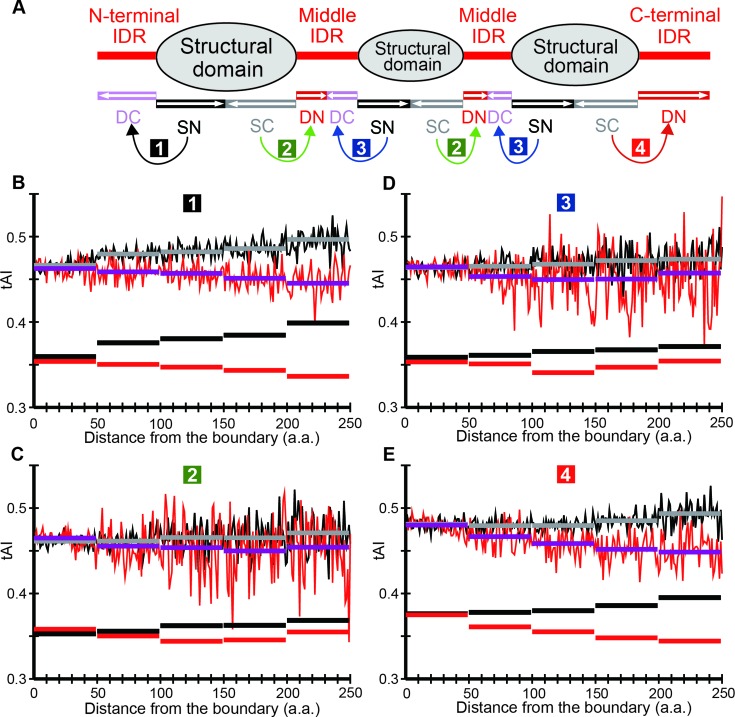
Figure 1.
How tAI means are calculated in the case of S. cerevisiae. (A) How proteins are divided into intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) and structural domains (SDs) and sub-classified according to their locations. Curved arrows indicate the pairs of IDR and SD sections for comparing distributions of mean tAI. (B) Comparison of the tAI mean distributions of N-terminal IDRs with contiguous SDs. (C) Comparison of the tAI mean distributions of the first half of middle IDRs with contiguous SDs. (D) Comparison of the tAI mean distributions of the latter half of middle IDRs with contiguous SDs. (E) Comparison of the tAI mean distributions of C-terminal IDRs with contiguous SDs. (B–E) The fluctuating red and black lines respectively represent tAIs in SDs and IDRs. The arithmetic means of each distance bin (1∼49, 50∼99, 100∼149, 150∼149 and 150∼ amino acid residues from the nearest IDR/SD boundary) for IDR and SD sections are indicated by magenta and grey horizontal bars, respectively, while the corresponding geometric means are shown in red and black horizontal rectangles.