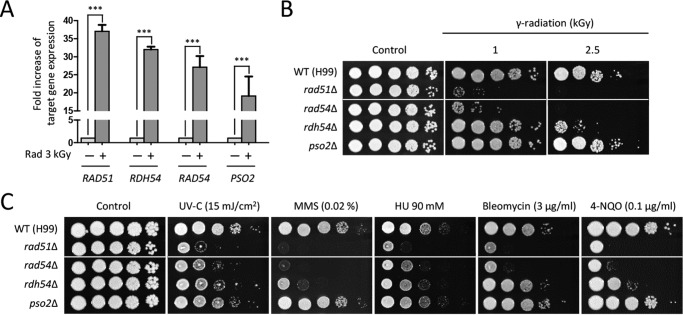
FIG 2 .
DNA repair response is critical for gamma radiation resistance. (A) Fold increase in expression of DNA repair-related genes exposed to gamma radiation. The fold increase of target gene expression was quantitatively measured by qRT analysis using the gene-specific primers listed in Table S2. The cDNA was synthesized with total RNAs extracted from cells recovered at 30 min after exposure to gamma radiation or not exposed to gamma radiation. Duplicate technical experiments with two or more biological samples were performed. Representative images from independent experiments for each DNA damage-responsive gene are shown. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate the statistical significance of differences in expression levels of each gene (***, P < 0.001). (B) Spotting assay for gamma radiation resistance. Cells cultured overnight in liquid YPD medium were serially spotted onto the solid YPD medium and then exposed to the indicated dose of gamma radiation. Exposed cells were further incubated at 30°C and photographed for 1 to 3 days. (C) Rdh54, Rad54, and Rig1 are required for DNA damage response in C. neoformans. The wild-type (WT [H99]) or rad51Δ (KW362), rdh54Δ (KW78), rad54Δ (KW26), and pso2Δ (KW22) mutant C. neoformans strains were grown overnight at 30°C in liquid YPD medium, and the 10-fold serially diluted cells were spotted onto YPD agar containing the indicated concentrations of genotoxic DNA damage insults. Cells were incubated at 30°C and photographed for 1 to 3 days. The two images split by a horizontal white line in each spot assay were obtained from the same plate (B and C).