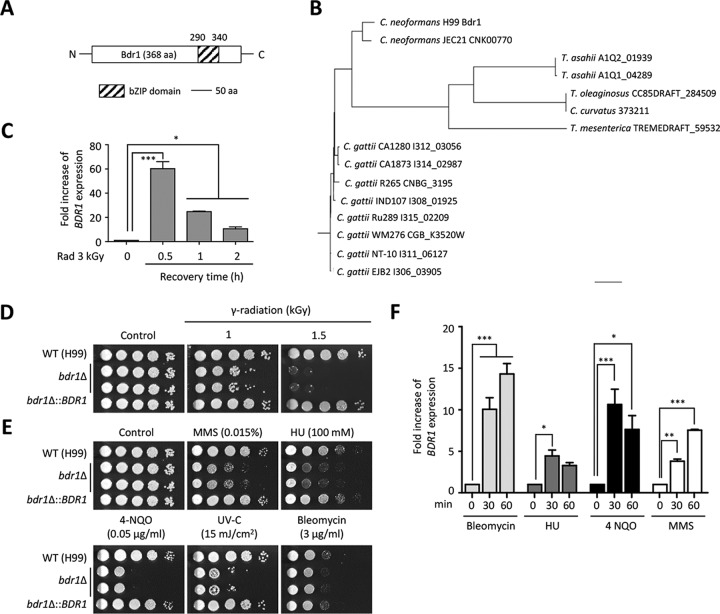
FIG 7 .
A novel TF, Bdr1, plays essential roles in both gamma radiation resistance and genotoxic DNA damage stress in C. neoformans. (A) The CNAG_02589 diagram shows the functional bZIP domain, which was identified by the Conserved Domain Search Service (CD Search; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi). (B) Phylogenetic tree of the Bdr1 homologs in fungi. The phylogenetic tree was generated by a philodendron phylogenetic tree printer (http://iubio.bio.indiana.edu/treeapp/treeprint-form.html). The scale bar represents an evolutionary distance of 0.1. (C and F) Fold increase of the BDR1 gene expression post-radiation exposure (3 kGy) and under genotoxic stress (bleomycin [3 µg/ml], HU [50 mM], MMS [0.02%], and 4-NQO [0.15 µg/ml]). (D and E) Bdr1 is required for both gamma radiation resistance and DNA damage stress. The WT (H99), bdr1Δ mutants (KW137 and KW138), and bdr1Δ::BDR1 complemented (KW193) C. neoformans strainswere grown overnight at 30°C in liquid YPD medium, and 10-fold serially diluted cells (1 to 104 dilutions) were spotted onto the YPD agar medium containing DNA damage stress inducers. For the UV-C and gamma radiation resistance test, serially diluted cells were exposed to gamma radiation or UV-C and then further incubated at 30°C for 1 to 3 days. For the qRT analysis, experiments with two or more biological samples were performed. Representative images from independent experiments for each gene are shown. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate statistical significance of differences in the relative expression levels (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001).